Unit 4.4
Segmentation
Presenter Notes
Segmentation
Objectives
- Shared memory
- Segmentation
Separate Instruction and Data Spaces
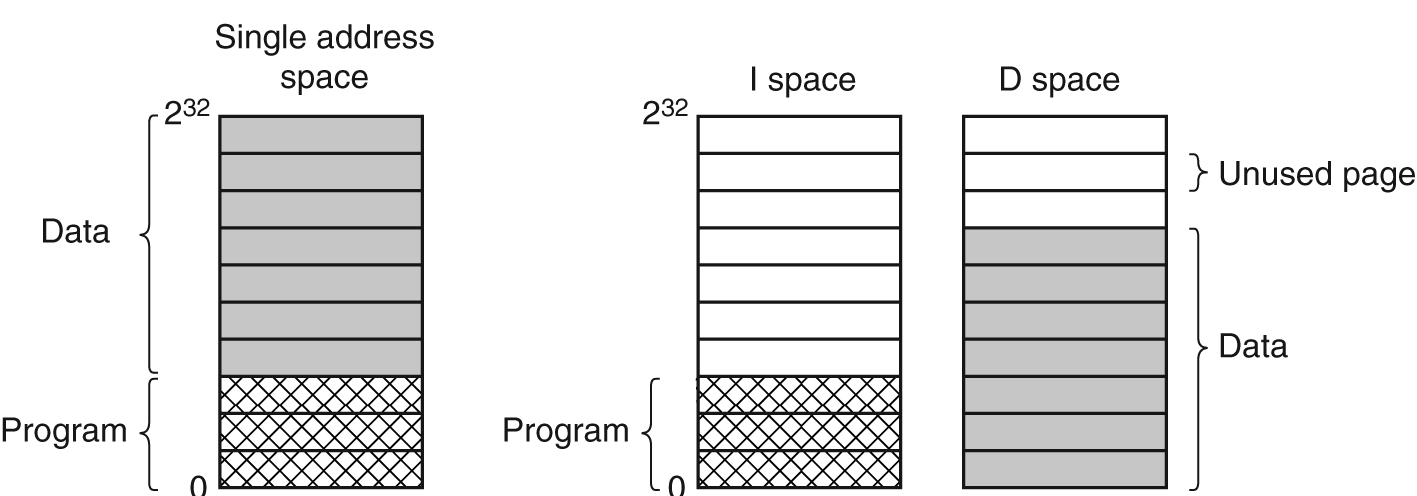
- (a) One address space. (b) Separate I and D spaces.
Presenter Notes
两种地址空间都可以进行分页,而且互相独立。它们分别有自己的页表,分别完成虚拟页面到物理页框的映射。
Shared Pages
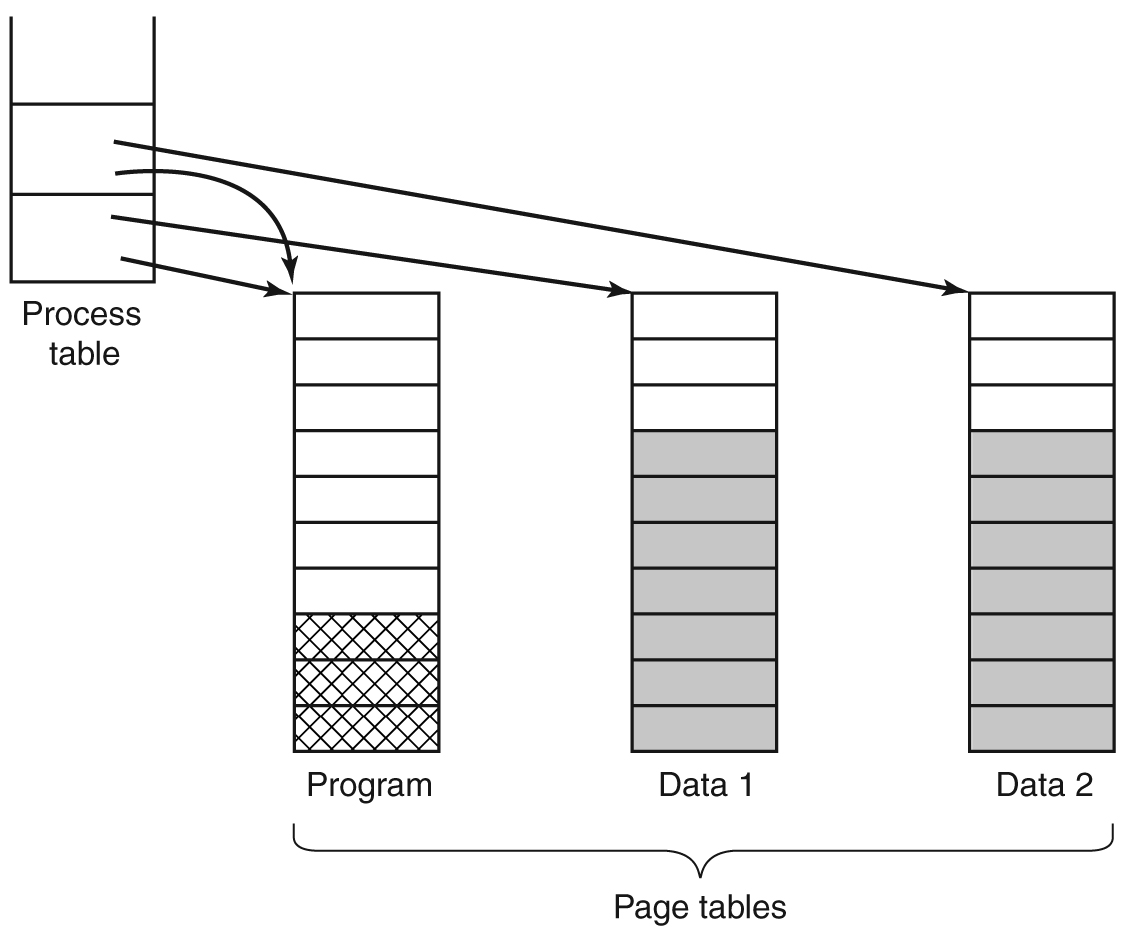
- Two processes sharing the same program sharing its page table.
Presenter Notes
几个不同的用户同时运行同一个程序很常见,由于避免了在内存中有一个页面的两份副本,共享页面效率更高。只读的页面(诸如程序文本)可以共享,但是数据页面则不能共享。
Shared Libraries
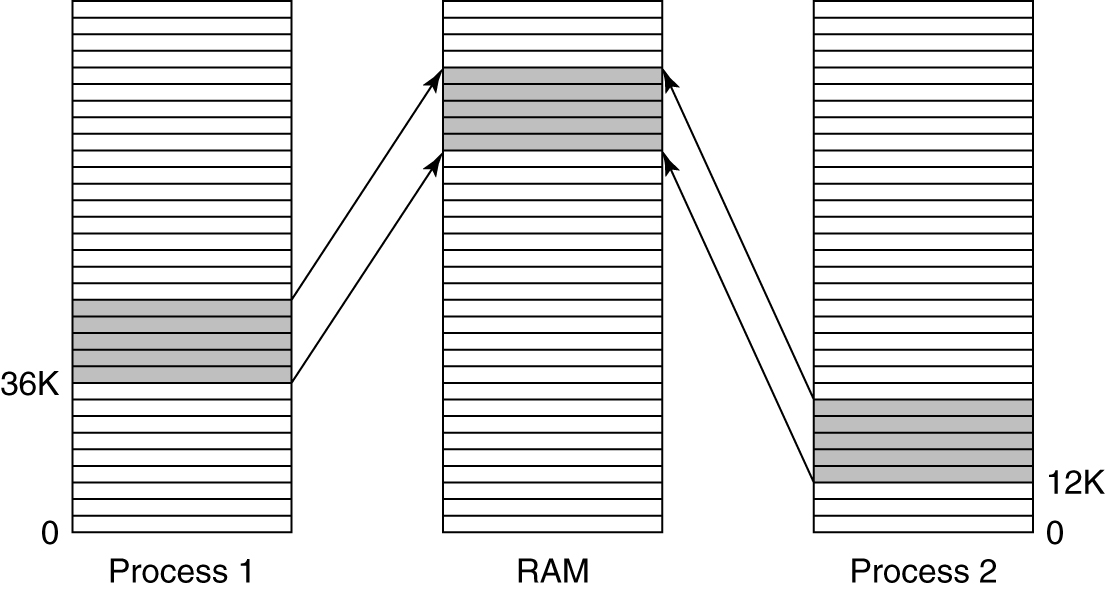
- A shared library being used by two processes.
Presenter Notes
如果一个程序被启动两次,大多数操作系统会自动共享所有的代码页面,而在内存中只保留一份代码页面的副本。由于库是共享的,因此在装载时再进行重定位就不可行,在编译时用一个特殊的编译选项告知编译器只产生使用相对地址的指令。
Segmentation (1)
A compiler has many tables that are built up as compilation proceeds, possibly including:
- The source text being saved for the printed listing (on batch systems).
- The symbol table – the names and attributes of variables.
- The table containing integer, floating-point constants used.
- The parse tree, the syntactic analysis of the program.
- The stack used for procedure calls within the compiler.
Presenter Notes
代码段由各个函数产生,函数的每一个语句将最终经过编绎和汇编生成二进制机器代码。这部分区域的大小在程序运行前就已经确定,并且内存区域通常属于只读,某些架构也允许代码段为可写,即允许修改程序。在代码段中,也有可能包含一些只读的常数变量,例如字符串常量等。
Segmentation (2)
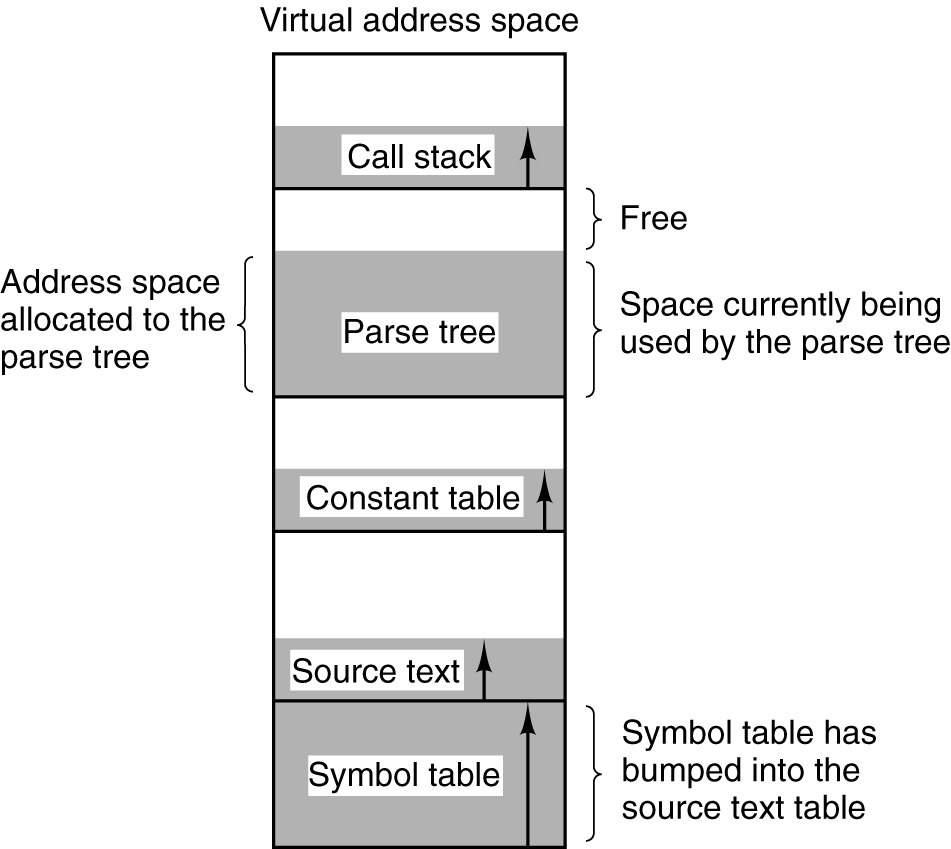
- In a one-dimensional address space with growing tables, one table may bump into another.
Presenter Notes
传入的参数、局部变量、都是在栈顶分布,随着子函数的增多而向下增长.
函数的调用地址(函数运行代码)、全局变量、静态变量都是在分配内存的低部存在
而malloc分配的堆则存在于这些内存之上,并向上生长.
Segmentation (3)
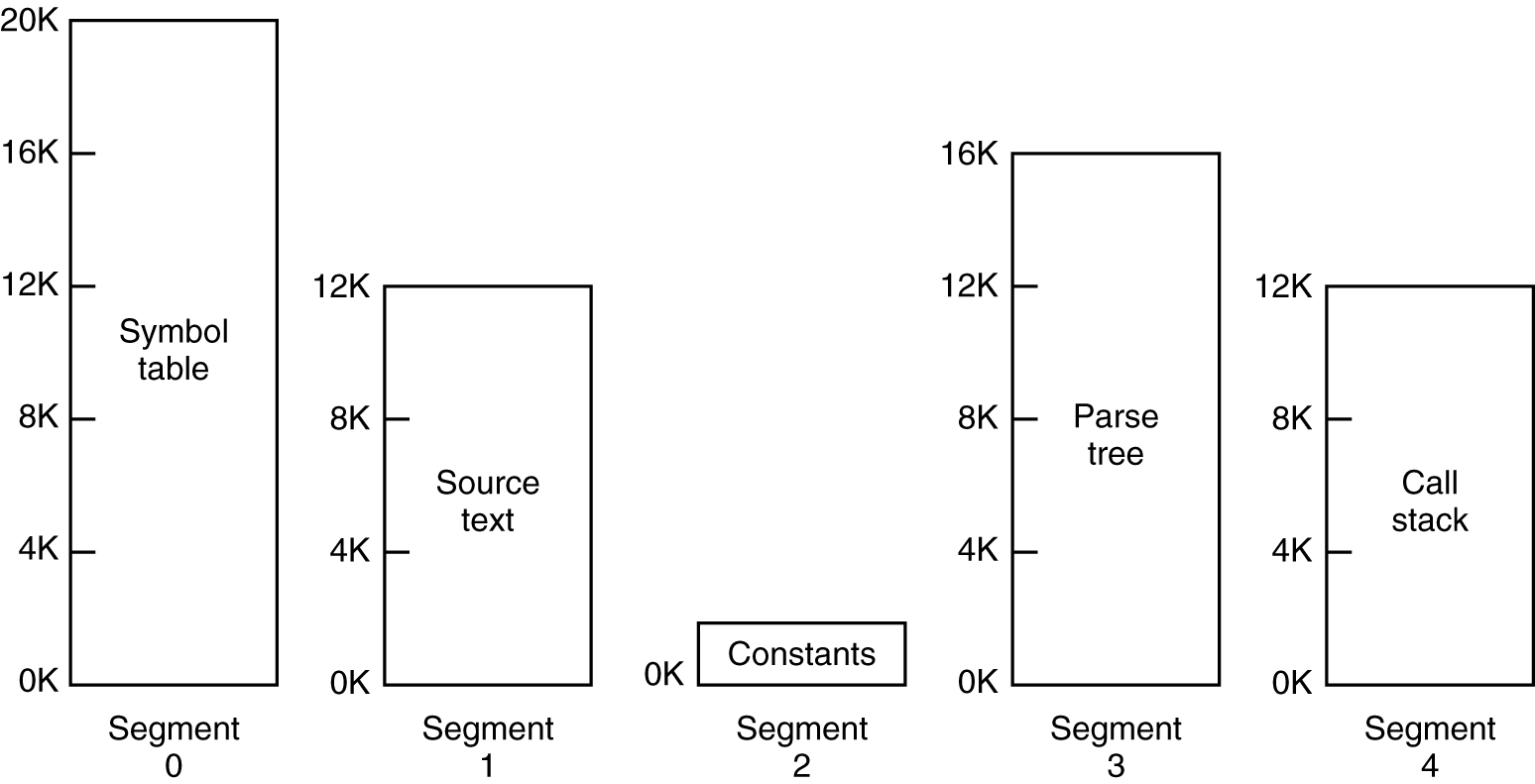
- A segmented memory allows each table to grow or shrink independently of the other tables.
Presenter Notes
分段内存允许每个表独立于其他表而增长或缩小。
Implementation of Pure Segmentation

- Comparison of paging and segmentation.
Presenter Notes
Segmentation
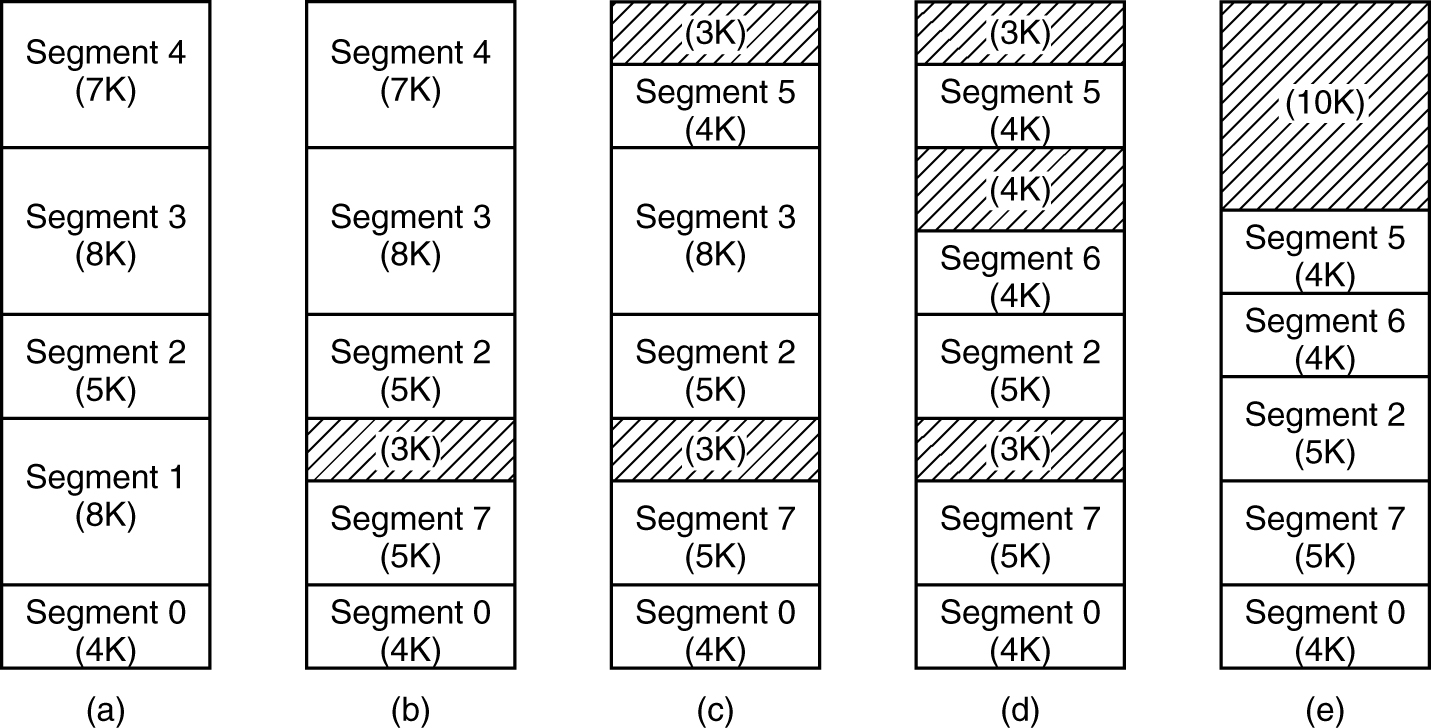
- (a)-(d) Development of checkerboarding. (e) Removal of the checkerboarding by compaction.
Presenter Notes
把程序按内容或过程(函数)关系分成段,每个段有自己的名字(编号)。段式管理以段为单位分配内存,然后通过地址变换将段式虚拟地址转换成实际的内存物理地址。
Summary
- Shared memory
- Segmentation
Segmentation with Paging
Objectives
- Segmentation with Paging
- Summary of variable memory management methods
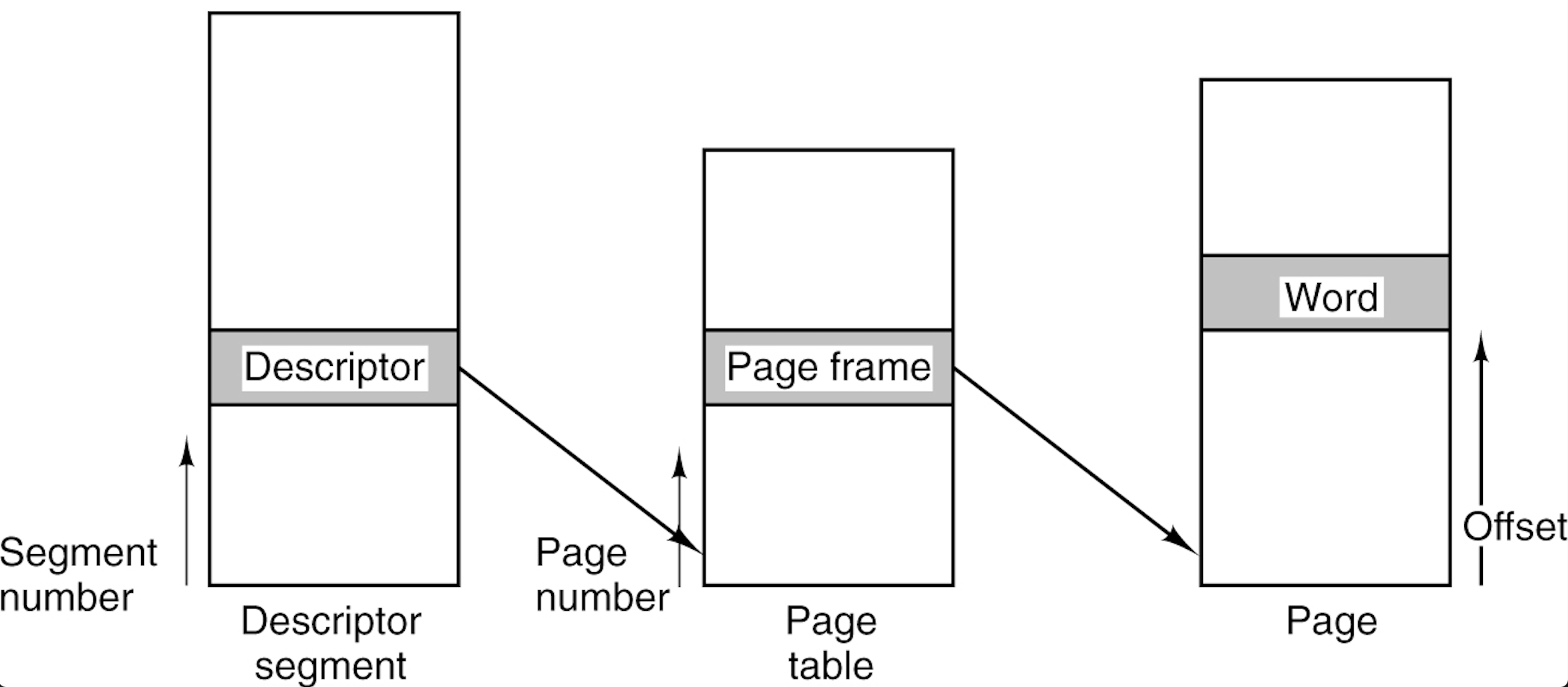
Segmentation with Paging
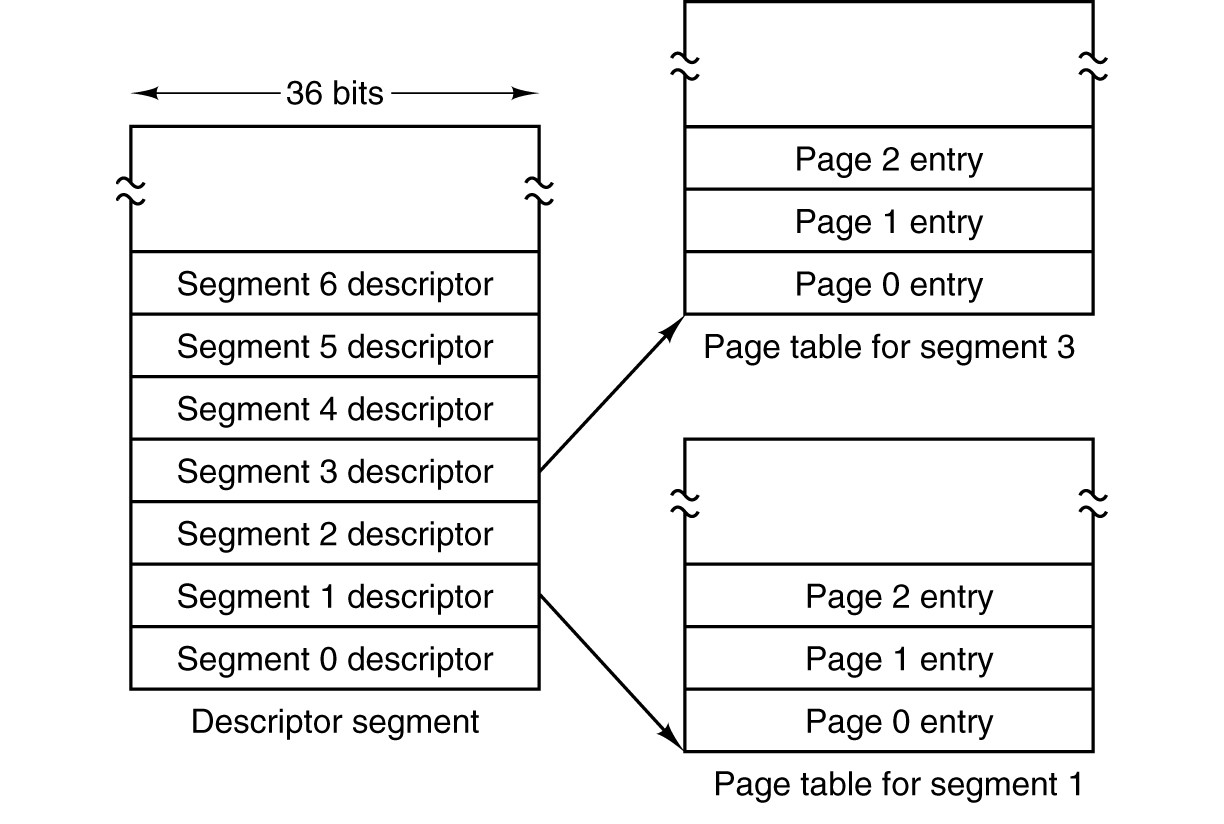
- The descriptor segment points to the page tables.
Presenter Notes
分页系统能有效地提高内存的利用率,而分段系统能反映程序的逻辑结构,便于段的共享与保护,将分页与分段两种存储方式结合起来,就形成了段页式存储管理方式。
Segmentation with Paging
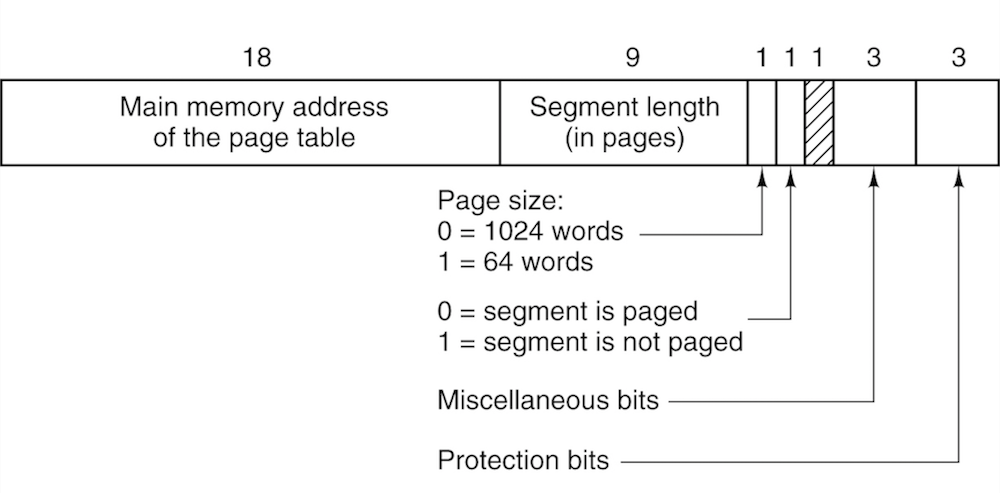
- A segment descriptor. The numbers are the field lengths.
Presenter Notes
在段页式存储管理系统中,作业的地址空间首先被分成若干个逻辑分段,每段都有自己的段号,然后再将每段分成若干个大小相等的页。对于主存空间也分成大小相等的页,主存的分配以页为单位。
Segmentation with Paging
When a memory reference occurs, the following algorithm is carried out:
- The segment number used to find segment descriptor.
- Check is made to see if the segment’s page table is in memory.
- If not, segment fault occurs.
- If there is a protection violation, a fault (trap) occurs.
- Page table entry for the requested virtual page examined.
- If the page itself is not in memory, a page fault is triggered.
- If it is in memory, the main memory address of the start of the page is extracted from the page table entry
- The offset is added to the page origin to give the main memory address where the word is located.
- The read or store finally takes place.
Presenter Notes
Segmentation with Paging

- A 34-bit virtual address.
- Conversion of a two-part address into a main memory address.
Presenter Notes
为实现段页式存储管理,系统应为每个进程设置一个段表,包括每段的段号,该段的页表始址和页表长度。每个段有自己的页表,记录段中的每一页的页号和存放在主存中的物理块号。
Segmentation with Paging: TLB
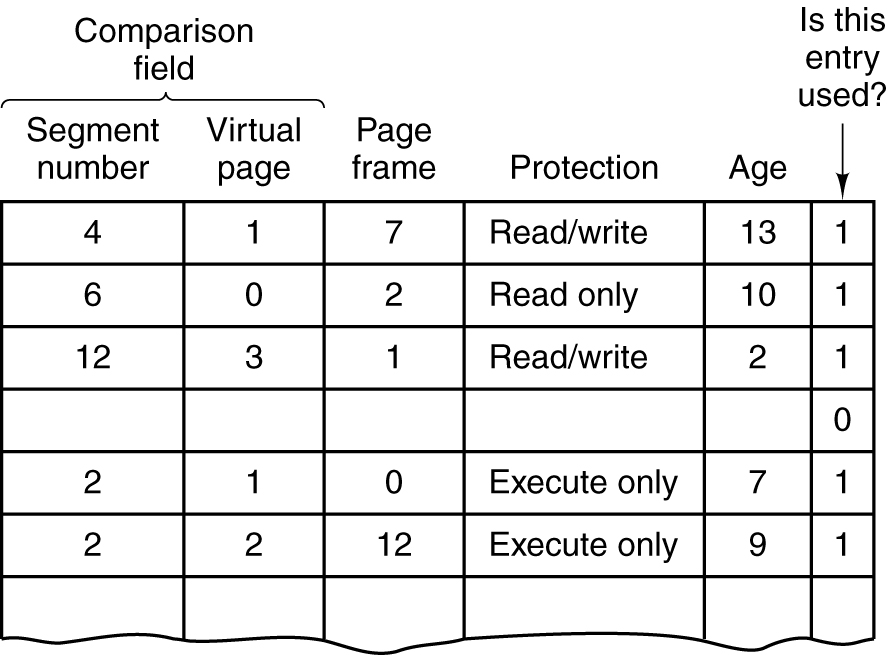
- A simplified version of the TLB. The existence of two page sizes makes the actual TLB more complicated.
Presenter Notes
Summary
- Summary of variable memory management methods
| Fixed Partition | Variable Partition | Paging | Segmentation | Segmentation with Paging | |
| Fragmen-tation | Internal | External | Internal | External | Internal |
| Continuity | Whole process | Whole process | Page | Segment | Page |
| Swapping | Whole process | Whole process | Page | Segment | Segment |
| Relocation | Base register | Base register | Page table | Segment table | Segment table with page tables |
Presenter Notes
Summary
- Segmentation with Paging
- Summary of variable memory management methods
Memory in x86
Objectives
- logical address
- linear address
- physical address
- Address translation
Intel Architechture 32
- logical address (48-bit)
- linear address (32-bit)
- physical address (32-bit)

- Address translation has two steps. It is NOT segmentation with paging.
Presenter Notes
从80386开始地址线变为了32位,可以支持虚拟存储器,支持实模式、保护模式,支持多任务,其内存寻址就开始采用虚拟寻址了。
IA32 Segment selector
- A segment selector is the segment register (16-bit).
- Segment selector is the index of segment descriptor table.
- Global Descriptor Table (up to 8192 entry)
- Local Descriptor Table (up to 8192 entry)

Presenter Notes
段寄存器CS、SS、DS、ES工作在实模式时与16位CPU的段寄存器作用相同,而工作在保护模式则不在存放段值,而是作为选择子,在虚拟地址转换时使用。FS和GS是附加数据段,通过把段地址存入这两个寄存器可以实现自定义寻址。
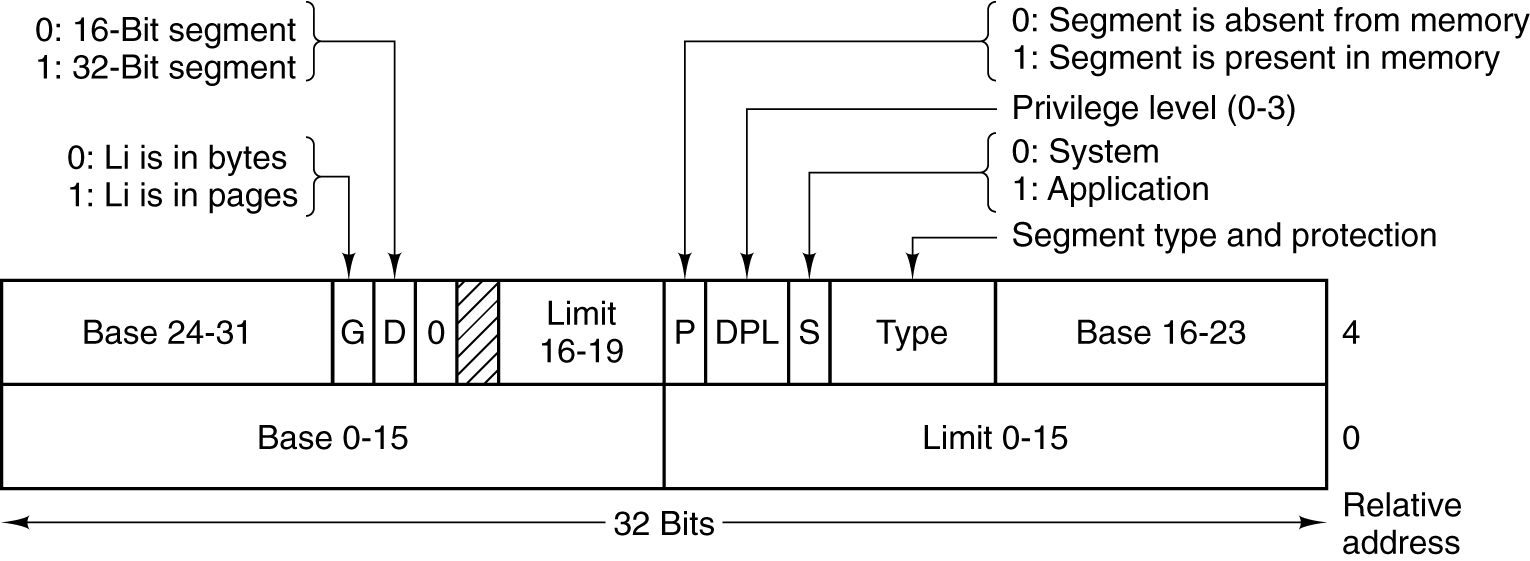
Segment descriptor table
- A segment descriptor is 64bit.
Presenter Notes
To linear address
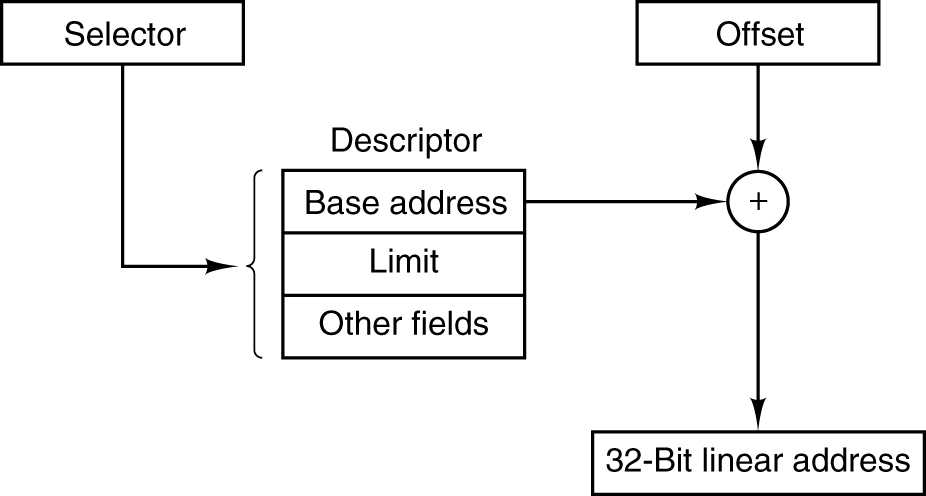
- Conversion of a (selector, offset) pair to a linear address.
Presenter Notes
逻辑地址是对应的硬件平台段式管理转换前地址,那么线性地址则对应了硬件页式内存的转换前地址。
To physical address
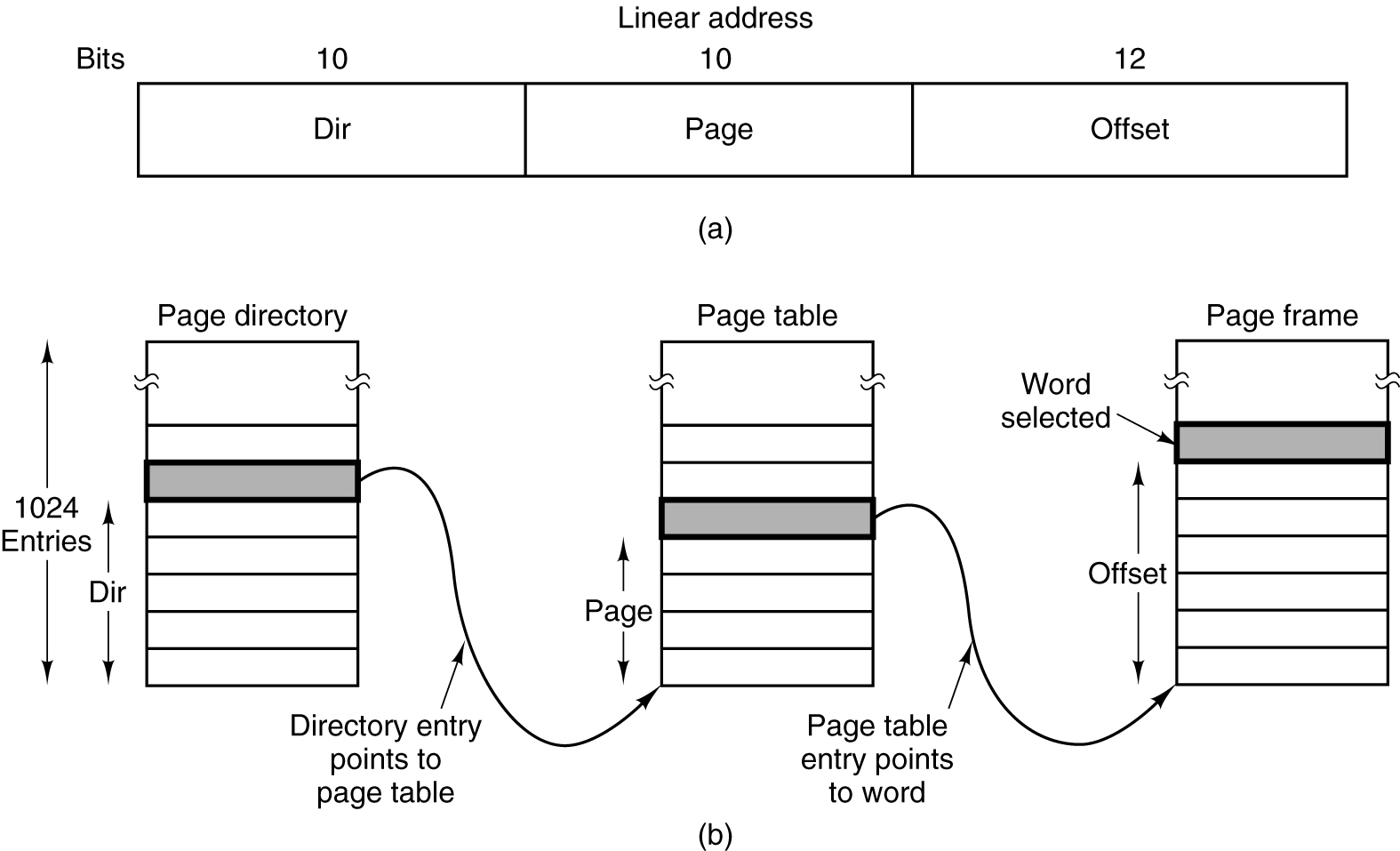
- Mapping of a linear address onto a physical address.
Presenter Notes
在Linux中称为存储器映射,同时提供了一个mmap的系统调用来实现该功能。
<<<<<<< HEAD
>>>>>>> ac0d0a59619cafcfe612cae65f8e65c030926e03
Protection
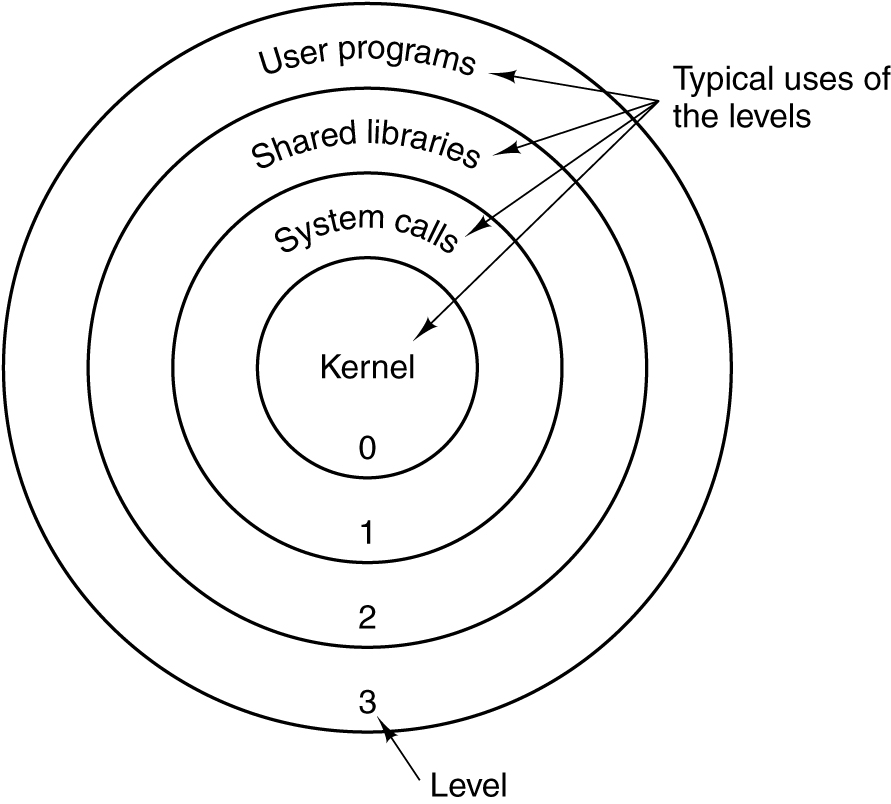
Presenter Notes
分级保护域经常被叫作保护环(Protection Rings),简称Rings。这是一种用来在发生故障时保护数据和功能,提升容错度,避免恶意操作 ,提升计算机安全的设计方式。
Summary
- logical address
- linear address
- physical address
- Address translation
Reference
- Chapter 3: Memory management, Modern Operating Systems . Forth Edition, Andrew S. Tanenbaum