Unit 2.2 File Permissions
Presenter Notes
Unit objectives
After completing this unit, you should be able to:
- Describe how permissions are used
- List the permissions required to perform several common commands
- Change permissions using symbolic and octal notation
- Describe how default permissions are calculated
Presenter Notes
学习目标:
- 理解权限是怎么用的
- 用一些指令来查看,列出权限
- 修改权限
- 描述缺省权限
File with users and groups
Objectives
- Users and groups
- File's owner and group
- View the file permissions
Users and groups

Presenter Notes
Linux系统是一个多用户多任务的分时操作系统,任何一个要使用系统资源的用户,都必须首先向系统管理员申请一个账号,然后以这个账号的身份进入系统。 用户的账号一方面可以帮助系统管理员对使用系统的用户进行跟踪,并控制他们对系统资源的访问;另一方面也可以帮助用户组织文件,并为用户提供安全性保护。 每个用户账号都拥有一个惟一的用户名和各自的口令。 用户在登录时键入正确的用户名和口令后,就能够进入系统和自己的主目录。 实现用户账号的管理,要完成的工作主要有如下几个方面: 用户账号的添加、删除与修改。 用户口令的管理。 用户组的管理。
The owner/group of a file/dir
- The default owner of a file/dir is the creator.
The default group of a file/dir is the primary group of the creator.
Who can change the owner/group of a file?
The root ONLY.
# chown newowner file[s]
# chgrp newgroup file[s]
# chown newowner:newgroup file[s]
# chown newowner.newgroup file[s]
Presenter Notes
- 文件缺省owner是当前文件的创造人
文件的所在的缺省组是当前创建文件者所在的组
只有root才能改文件的所属
Permissions
File permissions are assigned to:
- The owner of a file
- The members of the group the file is assigned to
- All other users
Permissions can only be changed by the owner and root!
Presenter Notes
Linux系统中的每个文件和目录都有访问许可权限,用他来确定谁能通过何种方式对文件和目录进行访问和操作。 文件或目录的访问权限分为只读,只写和可执行三种。 权限只可以被root用户与所有者改变
Viewing Permissions
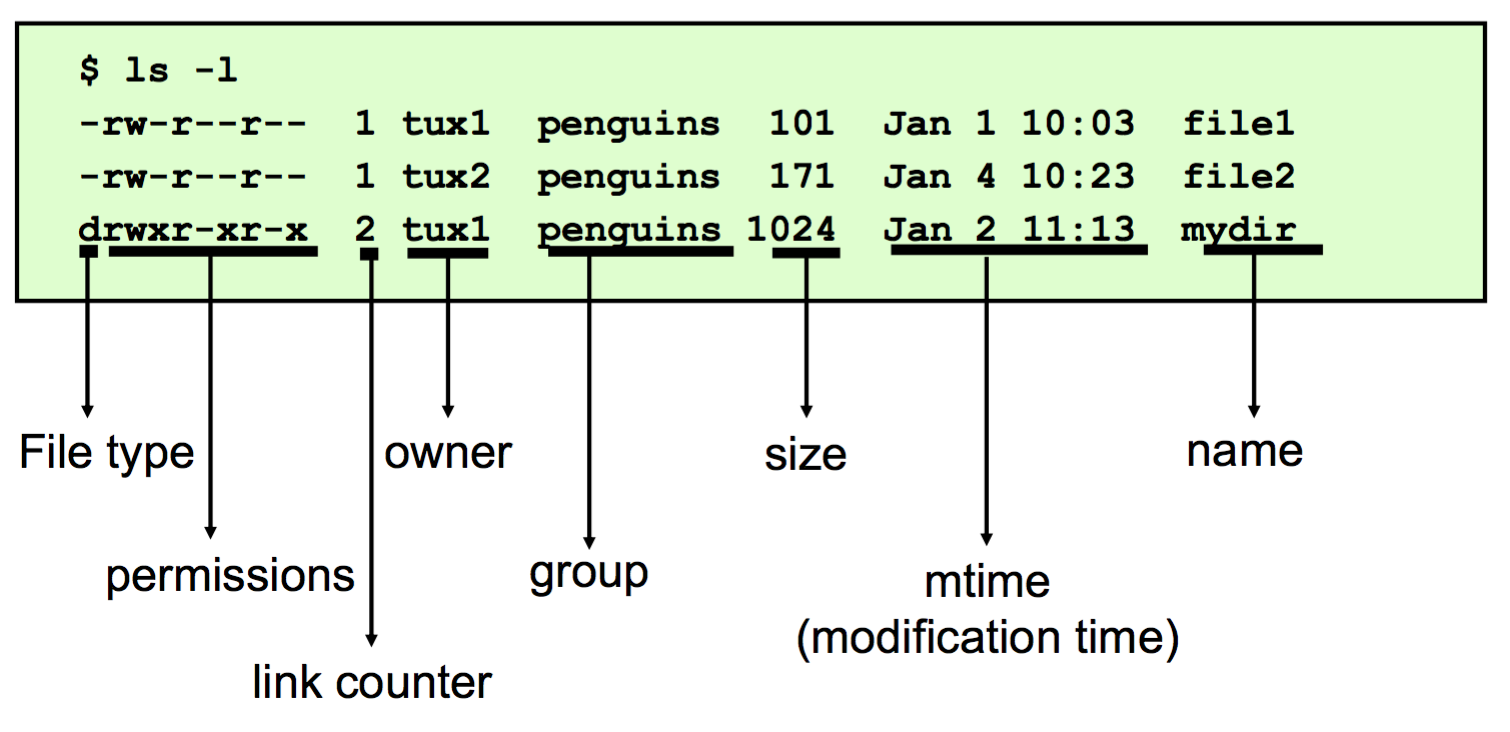
To show the permissions of a file, use the ls command with the -l option.
Presenter Notes
使用ls -l命令,可以查看文件的权限 使用 ls -l 命令查看文件的权限。在每一个文件的第一段为10位字母,第一个字母是文件的属性,"-"代表普通文件,"d"代表目录文件,"l"代表符号连接,"b""c"代表设备。后面9位为文件的权限,分为三段,分别代表“所有者(u)”、“同组人(g)”、“其它人(o)”的 读(r)、写(w)、执行(x)的权限。
Summary
- Users and groups
- Every user has one primary group, and may have extra groups (group set)
- View file's owner and group (ls)
- The creator is his file's owner by default. The default group for the file is the creator's primary group.
- Change the file's owner and group (chown)
- View the file permissions (ls)
Permissions
Objectives
- Permissions Notation
- Required permissions
Permissions Notation

Regular files:
r file is readable
w file is writeable
x file is executable (if in an executable format)
Directories:
r contents of directory can be listed (ls)
w contents can be modified (add/delete files)
x change into directory is possible (cd)
Presenter Notes
普通文件有r w x三种权限
目录文件也有r w x三种权限
文件的权限对三类人设定不同的权限:文件所有者、同组人、其它人。
对普通文件而言,"r"代表可以阅读文件内容,"w"代表可以修改或删除文件内容,"x"代表可以将文件作为命令来执行(同时需要r权限)。
对目录文件而言,"r"代表可以列出目录所包括的文件,"w"可以在目录内创建或删除文件(同时需要x权限),"x"表明目录可以做为活动目录。
Required permissions
| Command | Source directory | Source file | Target directory |
| ----------- | ---------------- | ----------- | ---------------- |
| cd | x | N/A | N/A |
| ls | x,r | N/A | N/A |
| mkdir,rmdir | x,w | N/A | N/A |
| cat, less | x | r | N/A |
| cp | x | r | x,w |
| cp -r | x,r | r | x,w |
| mv | x,w | None | x,w |
| vi | x,r | r,w | N/A |
| rm | x,w | None | N/A |
Question:
If you have all permissions on a directory, but have no permissions on the file in this directory:
- Can you read the file?
- Can you delete the file?
- Can you modify the file's content?
Presenter Notes
不同命令需要不同的文件权限,按照权限strict的程度进行使用
Summary
- Permissions Notation
- Read, Write, Execute for files and directories
- Required permissions
- Minimal permissions required for common commands to run
Change permissions
Objectives
- How to change the file permission?
- Who can change the file permission?
- What is the default permission for files and directories?
Change the file/directory permission
- chmod <MODE> <FILE[S]>
- Mode can be symbolic or octal.
- symbolic:
u(owner) , g(group), o(other), a(all);
+ / - / = ;
r(read), w(write), x(execute)
eg. chmod u+w,g-x,o= file1
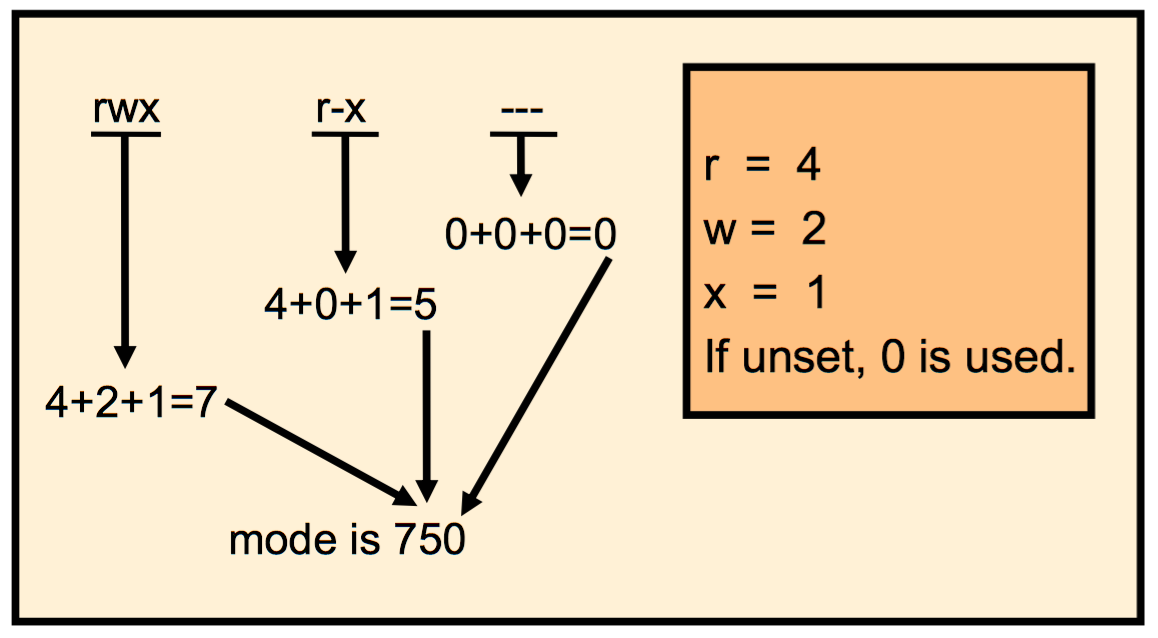
chmod 755 file1
Presenter Notes
可以使用符号或八进制数来设置文件权限
命令:chmod (change mode)
作用:修改文件的权限
格式:chmod [options] 符号权限或八进制权限files……
例如:使用符号来改变文件的权限。例如:chmod go-x doc 为删除doc文件的同组人和其它人的执行权。chmod u-x,go+w doc为删除doc文件所有者的执行权并添加同组人和其它人的写权。
使用八进制数来设置文件权限。三位八进制数,分别代表“所有者(u)”、“同组人(g)”、“其它人(o)”,读(r)、写(w)、执行(x)的权限用4,2,1代表。例:744代表rwxr--r--,666代表rw-rw-rw。
umask
- New files should not be created with 666! To avoid this problem, a permission mask exists.
Regular files:
| --------------------- | --------- | ---- |
| Default permissions | rw-rw-rw | 666 |
| umask (-) | ----w--w- | 022 |
| Resulting permissions | rw-r--r-- | 644 |
| --------------------- | --------- | ---- |
Directories:
| --------------------- | --------- | ---- |
| Default permissions | rwxrwxrwx | 777 |
| umask (-) | ----w--w- | 022 |
| Resulting permissions | rwxr-xr-x | 755 |
| --------------------- | --------- | ---- |
- Syntax: umask 022
Presenter Notes
umask(掩码)是在创建文件时设置缺省权限用的。创建普通文件时,由666减umask。创建目录的缺省权限,是由777减umask。对普通用户而言,umask=002,即新创建文件和目录的缺省权限分别为664和775。对root用户而言,umask=022,即新创建文件和目录的缺省权限分别为644和755。可以在/etc/profile内设定umask值。
使用umask设定文件和目录的缺省权限
Who can change permissions?
- The owner of the file or directory
- The root user
Presenter Notes
文件所有者以及root用户可以修改文件或者目录的权限
Summary
- Use
chownto change the file permission - Root and owner can change the file permission
- Umask is used to set the default permission for files and directories
Unit review
- Permissions determine whether a user is able to do something with a file or directory.
- Permissions can be set for the user, the group, and all others.
- Three base permissions exist: read, write, and execute.
- To view the permissions, use ls –l.
- Permissions can be changed only by the owner of the file or directory and by root.
- The umask determines the default permissions on a file.
Presenter Notes
- 权限决定了一个用户是否可以操作目录或者文件
- 用户,组,以及其它,都可以被设置权限
- 看文件的权限,用指令ls -l
- 权限是可以被改的,文件所有者或者root
- umask命令的使用
Unit summary
Having completed this unit, you should be able to:
- Describe how permissions are used
- List the permissions required to perform several common commands
- Change permissions using symbolic and octal notation
- Describe how default permissions are calculated
References
- Unit 5: File and Directory Permissions, Linux Basics and Installation , ERC 7.2, IBM