Unit 3.8
Deadlocks
Presenter Notes
Resources
- Preemptable and Nonpreemptable Resources
- Sequence of events required to use a resource:
- Request the resource.
- Use the resource.
- Release the resource.
Resource Acquisition
- Using a semaphore to protect resources.

- (a) One resource. (b) Two resources.
Resource Acquisition

- (a) Deadlock-free code. (b) Code with a potential deadlock.
Deadlock
Deadlock can be defined formally as follows:
- A set of processes is deadlocked if each process in the set is waiting for an event that only another process in the set can cause.
Conditions for Resource Deadlocks
- Mutual exclusion condition
- Hold and wait condition.
- No preemption condition.
- Circular wait condition.
Deadlock Modeling
Resource allocation graphs.
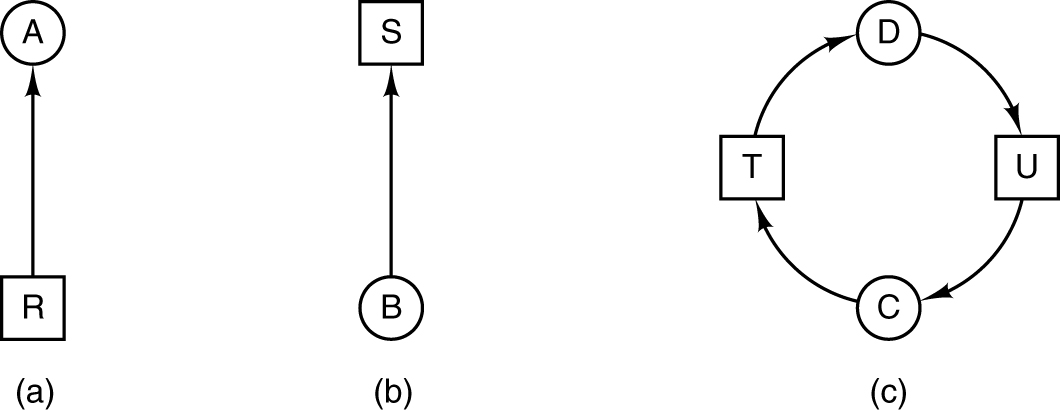
- (a) Holding a resource. (b) Requesting a resource. (c) Deadlock.
Deadlock Modeling
An example of how deadlock occurs and how it can be avoided.
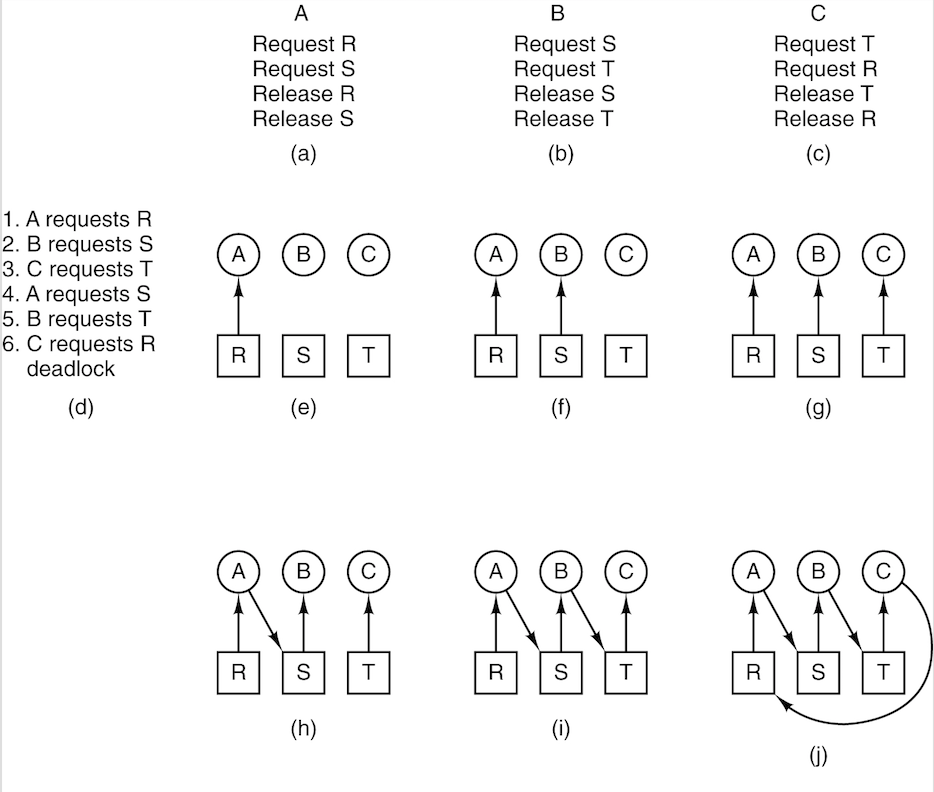
Strategies for dealing with deadlocks
- Just ignore the problem.
- Detection and recovery. Let deadlocks occur, detect them, take action.
- Dynamic avoidance by careful resource allocation.
- Prevention, by structurally negating one of the four required conditions.
Deadlock Detection
- Deadlock Detection with One Resource of Each Type

- (a) A resource graph. (b) A cycle extracted from (a).
Deadlock Detection
Deadlock Detection with Multiple Resources of Each Type

- The four data structures needed by the deadlock detection algorithm.
Deadlock Detection
An example for the deadlock detection algorithm.

Recovery from Deadlock
- Recovery through preemption
- Recovery through rollback
- Recovery through killing processes
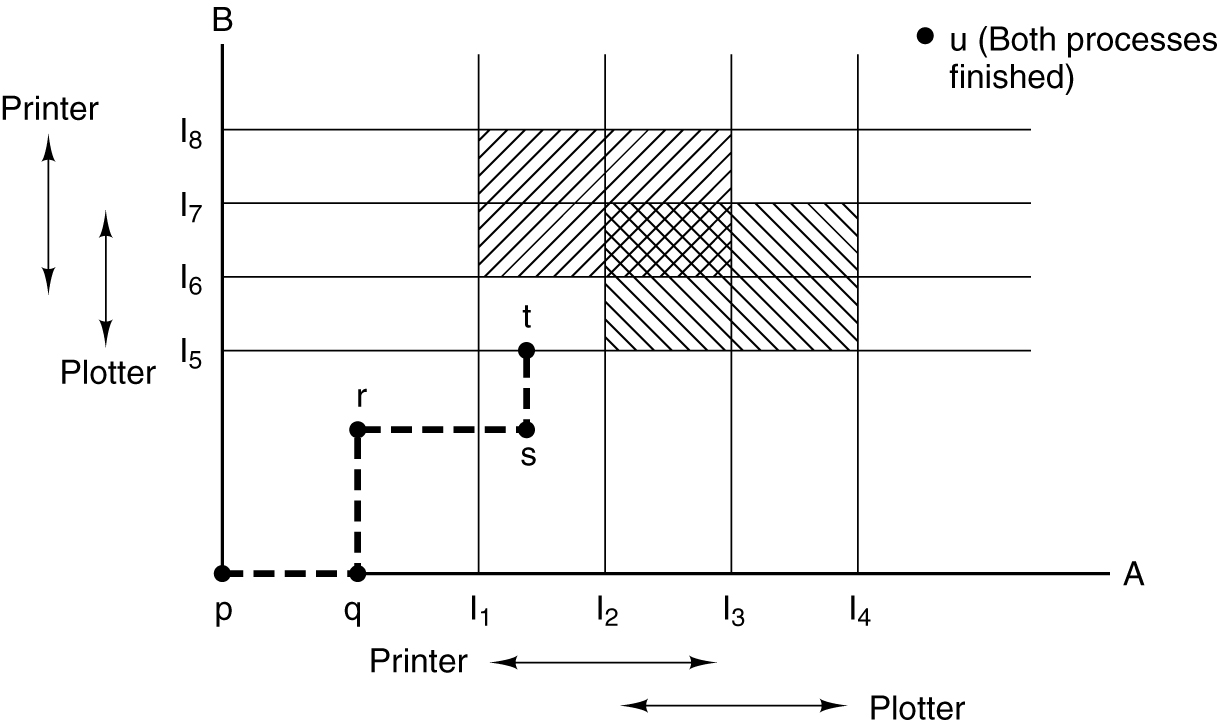
Deadlock Avoidance
- Two process resource trajectories.
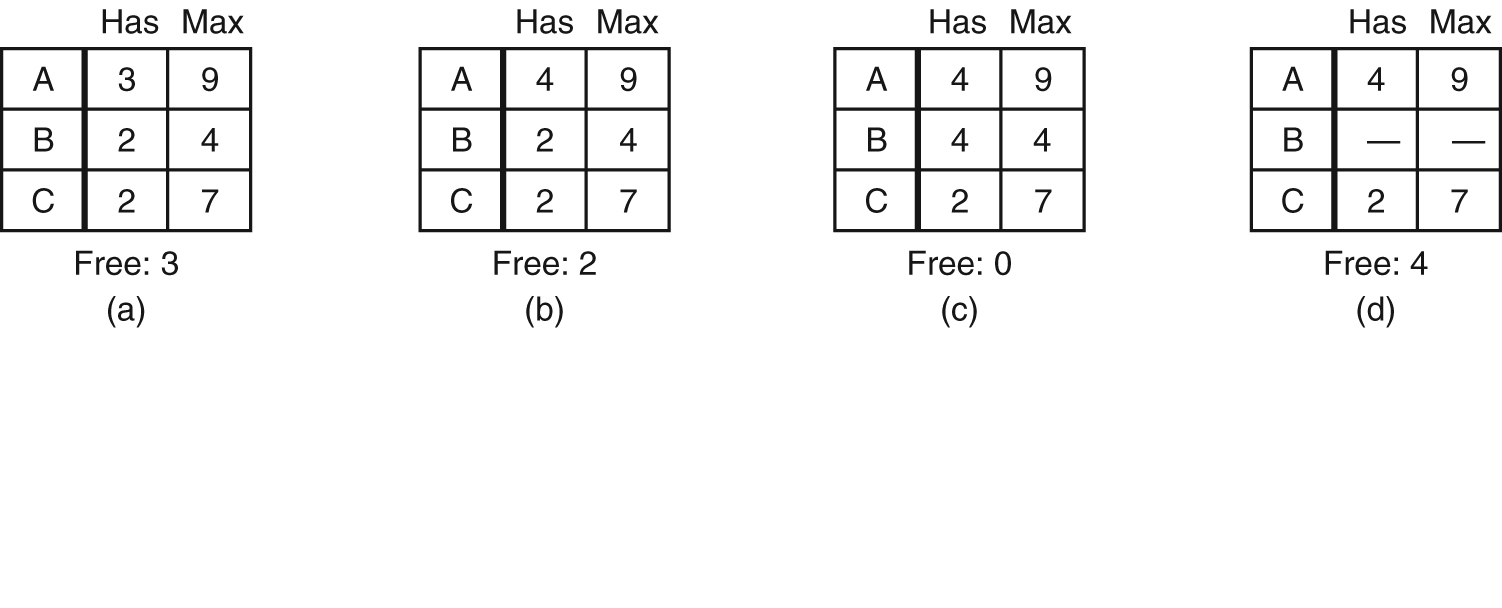
Safe and Unsafe States
- Demonstration that the state in (a) is safe.
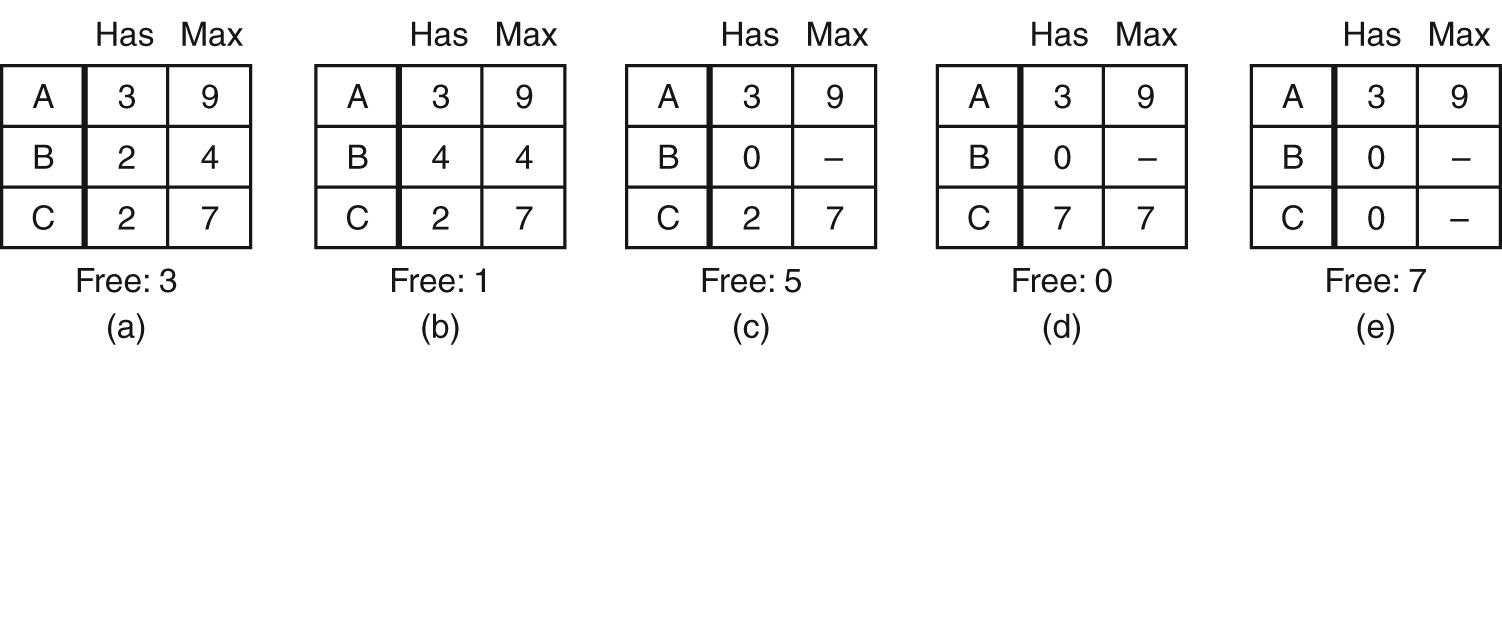
Safe and Unsafe States
- Demonstration that the state in (b) is not safe.
The Banker’s Algorithm
- The Banker’s Algorithm for a Single Resource
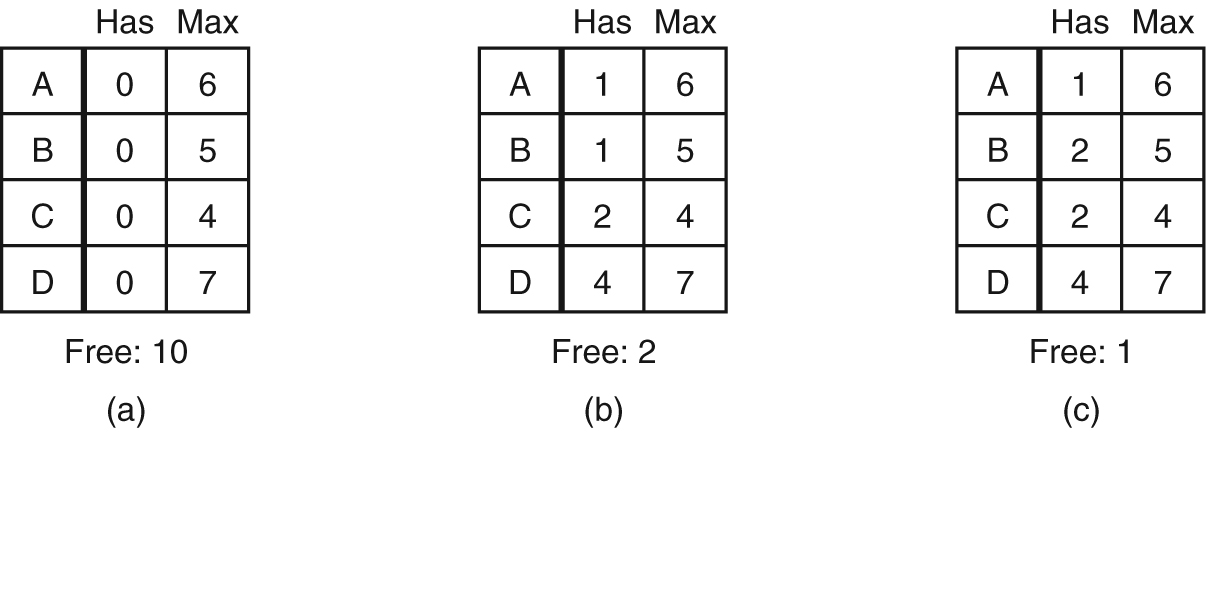
- Three resource allocation states: (a) Safe. (b) Safe. (c) Unsafe.
The Banker’s Algorithm
- The banker’s algorithm with multiple resources.

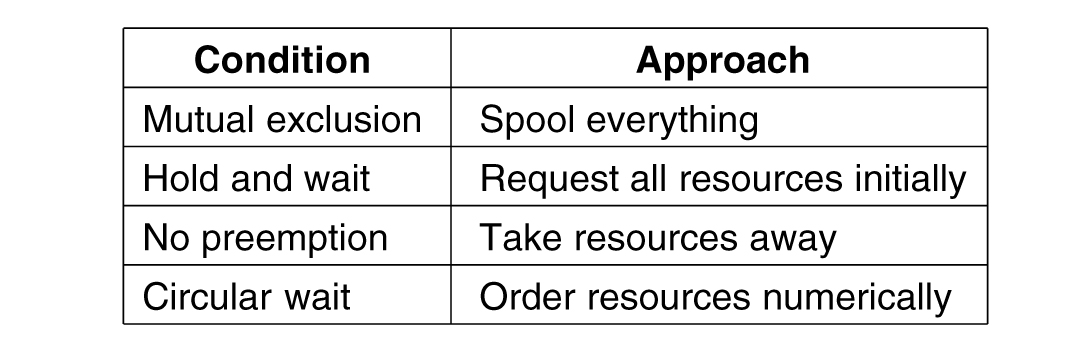
Deadlock Prevention
- Attacking the mutual exclusion condition
- Attacking the hold and wait condition
- Attacking the no preemption condition
- Attacking the circular wait condition
Reference
- Chapter 6: Deadlocks, Modern Operating Systems . Forth Edition, Andrew S. Tanenbaum