Unit 3.3
Scheduling
Presenter Notes
Process Behavior
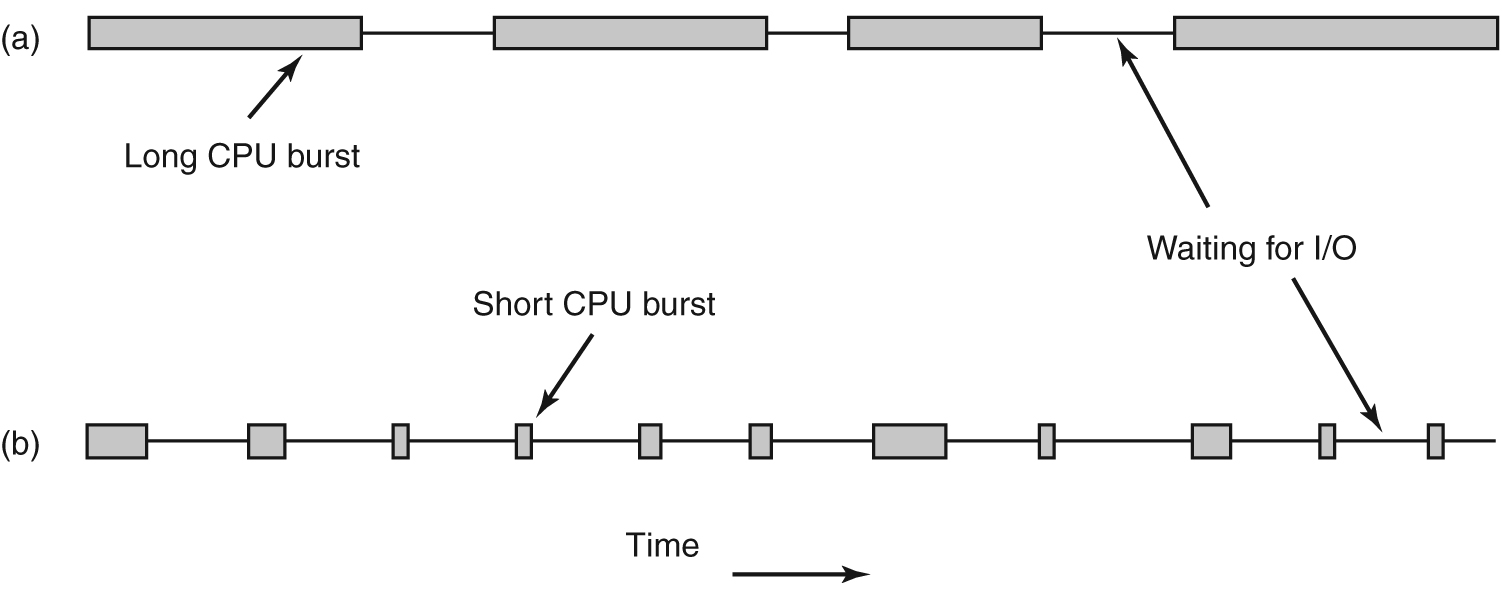
Bursts of CPU usage alternate with periods of waiting for I/O.
(a) A CPU-bound process.
(b) An I/O-bound process.
Presenter Notes
几乎所有的进程的(磁盘)I/O请求或计算都是交替突发的,典型的,CPU不停顿的运行一段时间,然后发出一个系统调用以便读写文件。
Scheduling Algorithm Goals
Some goals of the scheduling algorithm under different circumstances.

Presenter Notes
进程调度所采用的算法是与整个系统的设计目标相一致的: 1.批处理系统:增加系统吞吐量和提高系统资源的利用率; 2.分时系统:保证每个分时用户能容忍的响应时间。 3.实时系统:保证对随机发生的外部事件做出实时响应。
Scheduling in Batch Systems
Batch Systems are usually non-preemptible.
- First Come First Served
- Shortest Job First
- Shortest Remaining-time Next
- High Response-ratio First
Presenter Notes
1.先来先服务 2.最短作业优先 3.最短剩余时间优先 4.高响应比优先
Parameters in scheduling algorithm
- Arrival time / Finish time (point)
- Waiting time / Executing time (period)
- Turnaround time = Waiting time + Executing time = Finish time – Arrival time
- Weighting turnaround time = Turnaround time / Executing time
- Response ratio = Turnaround time / Executing time = 1 + Waiting time / Executing time
Scheduling in Interactive Systems
- Round-robin scheduling
- Priority scheduling
- Multiple queues
- Shortest process next
- Guaranteed scheduling
- Lottery scheduling
- Fair-share scheduling
Presenter Notes
1.轮转调度 2.优先级调度 3.多级队列 4.最短进程优先 5.保证调度 6.彩票调度 7.公平分享调度
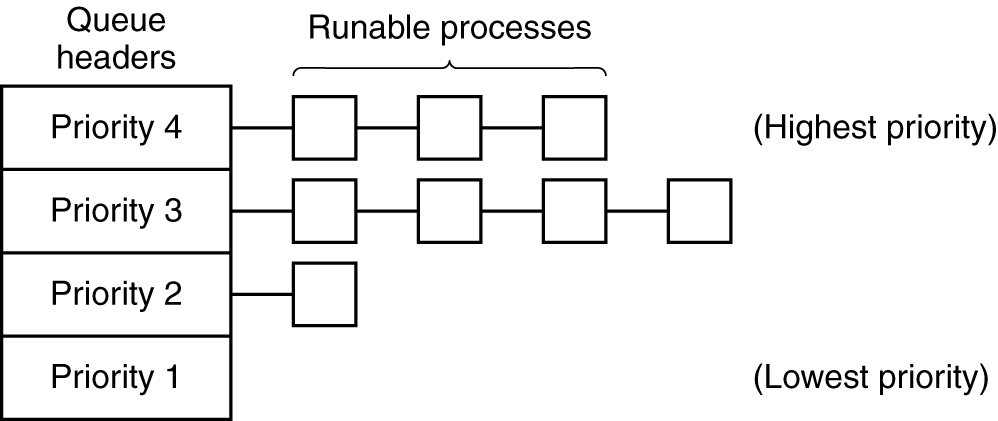
Priority Scheduling
A scheduling algorithm with four priority classes.
Presenter Notes
只要存在优先级为第四类的可运行进程,就按照轮转算法为每个进程运行一个时间片,此时不例会较低优先级的进程。若第四类进程为空,则按照轮转算法运行第三类进程。若第四类和第三类均为空,则按照轮转法运行第二类进程。如果不偶尔对优先级进行调整,则低优先级进程很可能会产生饥饿现象
Reference
- Chapter 2: Processes and threads, Modern Operating Systems . Forth Edition, Andrew S. Tanenbaum