Chapter 3. Process Management
- Unit 7.1 Shell basics
- Unit 7.2 Unix utilities
- Unit 7.3 Shell scripting
Unit 7.1 Shell Basics
Presenter Notes
Unit objectives
After completing this unit, you should be able to:
- Explain the function of the shell
- Discuss metacharacters and reserved words
- Use wildcards to access files with similar names
- Use redirection and pipes
- Use command substitution
- Describe and use the most common filters
- Group commands to control their execution
- Work with shell variables
- Use aliases
- Apply quoting
Shell features
When the user types a command, various things are done by the shell before the command is actually executed.
- Wildcard expansion
- Input/output redirection
- Command grouping
- Line continuation
- Shell variable expansion
- Alias expansion
- Shell scripting
For example, the ls *.doc command could be expanded to /bin/ls --color=tty mydoc.doc user.doc before execution (depending on settings and files present). -
Presenter Notes
Shell的概念最初是在Unix操作系统中形成和得到广泛应用的。Unix的Shell有很多种类,Linux系统继承了Unix系统中Shell的全部功能,现在默认使用的是bash。 Shell具有如下突出特点: (1)把已有命令进行适当组合构成新的命令。 (2)提供了文件名扩展字符(通配符,如* 、 ?、 [ ]),使得用单一的字符串可以匹配多个文件名,省去键入一长串文件名的麻烦。 (3)可以直接使用Shell的内置命令,而不需创建新的进程,如Shell中提供的cd、echo、exit、pwd、kill等命令。为防止因某些Shell不支持这类命令而出现麻烦,许多命令都提供了对应的二进制代码,从而也可以在新进程中运行。 (4)Shell允许灵活地使用数据流,提供通配符、输入/输出重定向、管道线等机制,方便了模式匹配、I/O处理和数据传输。 (5)结构化的程序模块,提供了顺序流程控制、条件控制、循环控制等。 (6)Shell提供了在后台执行命令的能力。 (7)Shell提供了可配置的环境,允许创建和修改命令、命令提示符和其它的系统行为。 (8)Shell提供了一个高级的命令语言,能够创建从简单到复杂的程序。这些Shell程序称为Shell脚本,利用Shell脚本,可把用户编写的可执行程序与Unix命令结合在一起,当作新的命令使用,从而便于用户开发新的命令。
Metacharacters and reserved words
Metacharacters are characters that the shell interprets as having a special meaning.
- Examples: < > | ; ! ? * $ \ ` ' " ~ [ ] ( ) { }
Reserved words are words that the shell interprets as special commands.
- Examples: case, do, done, elif, else, esac, for, fi, function, if, in, select, then, until, while
Presenter Notes
shell 除了有通配符之外,由shell 负责预先先解析后,将处理结果传给命令行之外,shell还有一系列自己的其他特殊字符。
Basic wildcard expansion
When the shell encounters a word that contains a wildcard, it tries to expand this to all matching file names in the given directory. Hidden files are ignored.
Example:
. .. .et .w few myfile ne nest net new test1 test1.2 test1.3? matches a single character
$ ls ne?==>net new
$ ls ?e?==>few net new* matches any string, including the null string
$ ls n*==>ne nest net new
$ ls *w==>few new
Presenter Notes
它是由shell解析,并且一般用于匹配文件名,实际上就是shell解释器去解析的特殊符号,linux系统通配符有几下几种: *:匹配任意多个字符 ?:匹配任意一个字符 [...]:匹配中括号内出现的任意一个字符 [!...]:不匹配中括号内出现的任意一个字符
- 一般出现在要shell命令或脚本中,匹配特定的文件名
Advanced wildcard expansion
The wildcards [, ], -, and ! match a sigle character in inclusive lists.
Examples:
. .. .et .w few myfile ne nest net new test1 test1.2 test1.3$ ls ne[stw]==>net new$ ls *[1-5]==>test1 test1.2 test1.3$ ls [!tn]*==>few myfile$ ls ?[!y]*[2-5]==>test1.2 test1.3
Presenter Notes
通配符是由shell处理的(不是由所涉及到命令语句处理的,其实我们在shell各个命令中也没有发现有这些通配符介绍), 它只会出现在 命令的“参数”里(它不用在 命令名称里, 也不用在 操作符上)。当shell在“参数”中遇到了通配符时,shell会将其当作路径或文件名去在磁盘上搜寻可能的匹配:若符合要求的匹配存在,则进行代换(路径扩展);否则就将该通配符作为一个普通字符传递给“命令”,然后再由命令进行处理。总之,通配符 实际上就是一种shell实现的路径扩展功能。在 通配符被处理后, shell会先完成该命令的重组,然后再继续处理重组后的命令,直至执行该命令。
Quiz
Answer the following question :
0 1 2 9 10 11 99 100 101$ ls [100]*===> ???
File descriptors
- Every program has a number of file descriptors associated with it.
- Three descriptors are assigned by the shell when the program starts (STDIN, STDOUT, and STDERR).
- Other descriptors are assigned by the program when it opens files.
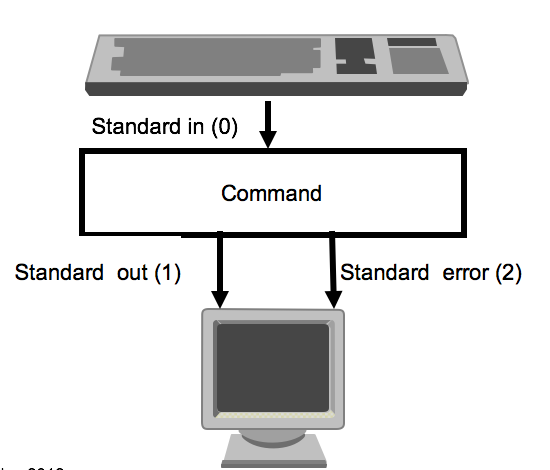
Presenter Notes
文件描述符是一个简单的整数,用以标明每一个被进程所打开的文件和socket。第一个打开的文件是0,第二个是1,依此类推。Unix 操作系统通常给每个进程能打开的文件数量强加一个限制。更甚的是,unix 通常有一个系统级的限制。
Output redirection
Default standard output: /dev/tty
$ ls==> displayfile1 file2 file3on the screenRedirect output to a file (override if file exist) :
$ ls > /tmp/ls.out==> storefile1 file2 file3inls.outRedirect and append output to a file:
$ ls >> /tmp/ls.out
Presenter Notes
有时候并不希望执行结果输出到屏幕。我想输出到文件或其它设备。这个时候我们就需要进行输出重定向了。
linux shell下常用输入输出操作符是: 标准输入 (stdin) :代码为 0 ,使用 < 或 << ; /dev/stdin -> /proc/self/fd/0 0代表:/dev/stdin 标准输出 (stdout):代码为 1 ,使用 > 或 >> ; /dev/stdout -> /proc/self/fd/1 1代表:/dev/stdout 标准错误输出(stderr):代码为 2 ,使用 2> 或 2>> ; /dev/stderr -> /proc/self/fd/2 2代表:/dev/stderr
Input redirection
write a message to all logged in users.
$ wall
Let's go to lunch!
<ctrl-d>now store the message in a file , then
$ wall < message
send a email
$ mail -s subject boss < mail_body.txt
Presenter Notes
当然有,命令默认从键盘获得的输入,改成从文件,或者其它打开文件以及设备输入。执行这个命令,将标准输入0,与文件或设备绑定。将由它进行输入。
Redirection in cat
Create a file with redirection:
$ cat > newfile
save me in the file...
<ctrl-d>
STDIN redirected from file:
$ cat < cities
Atlanta
Chicago
Default standard input:
$ cat
Atlanta
Atlanta
Chicago
Chicago
<ctrl-d>
Presenter Notes
cat命令的用途是连接文件或标准输入并打印。这个命令常用来显示文件内容,或者将几个文件连接起来显示,或者从标准输入读取内容并显示,它常与重定向符号配合使用。
cat file1 vs cat < file1
!C
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define BUFSIZE 512
int main(int argc,char** argv){
int n,fildes; char buf[BUFSIZE];
if (argc == 2){
fildes = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
} else {
fildes = STDIN_FILENO;
}
while ( (n=read(fildes,buf,BUFSIZE))>0) {
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO,buf,n)!=n){
printf("write error");
}
}
}
Error redirection
- Default standard error: /dev/tty
$ cat fileA
cat: fileA: No such file or directory - Redirect error output to a file:
$ cat fileA 2> error.file
$ cat error.file
cat: fileA: No such file or directory - Redirect and append errors to a file:
$ cat fileA 2>> error.file - Discard error output:
$ cat fileA 2> /dev/null
Presenter Notes
2> 将一个标准错误输出重定向到一个文件或设备 覆盖原来的文件 b-shell 2>> 将一个标准错误输出重定向到一个文件或设备 追加到原来的文件 2>&1 将一个标准错误输出重定向到标准输出 注释:1 可能就是代表 标准输出
& 将一个标准错误输出重定向到一个文件或设备 覆盖原来的文件 c-shell |& 将一个标准错误 管道 输送 到另一个命令作为输入
Combined redirection
- Combined redirects
$ cat < cities > cities.copy 2> error.file
$ cat >> cities.copy 2>> error.file < morecities - Association
- This redirects STDERR to where STDOUT is redirected.
$ cat cities > cities.copy 2>&1
...writes both stderr and stdout to cities.copy - be careful about this:
$ cat cities 2>&1 > cities.copy
...writes stderr to /dev/tty and stdout to cities.copy
- This redirects STDERR to where STDOUT is redirected.
Presenter Notes
bash 命令执行的时候有输出的数据会出现,那么如果这群数据必需要经过几道手续之后才能得到我们所想要的格式,应该如何来设定?这就牵涉到管线命令的问题了( pipe )
Pipes
A sequence of two or more commands separated by a vertical bar (|) is called a pipe or pipeline.
$ ls -l | wc -l
$ ps aux | wc -l
$ who | wc -lThe standard output of command1 becomes the standard input of command2.
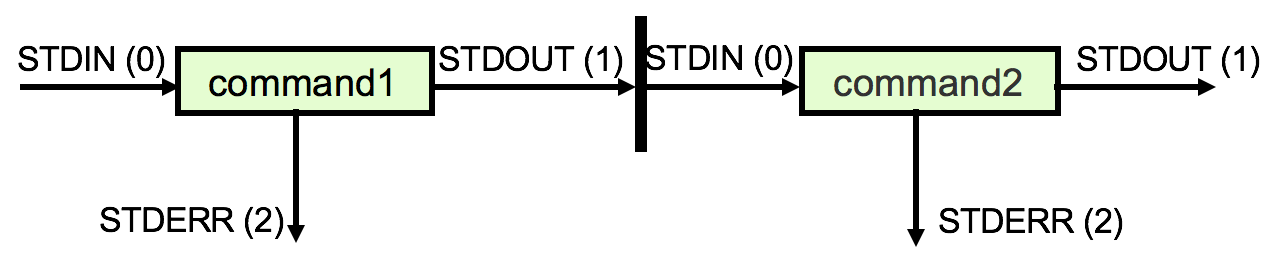
Presenter Notes
1、管道连接着处理元素,一个处理元素的输出是下一个处理处理元素的输入。 2、管道能加快数据处理速度。
Filters
A filter is a command that reads from standard in, transforms the input in some way, and writes to standard out. They can, therefore, be used at intermediate points in a pipeline.
$ ls | grep doc | wc -l
$ echo hello | tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'
$ ps aux | tee out | wc -l
Presenter Notes
1、是指用于处理流的程序。尽管 filter 可以单独使用,但是他们常常通过管道,组合起来使用。
2、默认从标准输入( standard input )获取数据,写到标准输出( standard output )。可以通过输入操作符 < 改变数据源,通过输出操作符 > 改变写入目标,通过追加操作符 >> 追加数据。
3、通过管道符 | ,链接多个 Filter。
Command substitution
- Command substitution allows you to use the output of a command as arguments for another command.
Use backticks -- ` -- or $() notation.
$ rm -i `ls *.doc | grep tmp`
$ echo There are $(ps ax | wc -l) processes running.
Command grouping
Multiple commands can be entered on the same line, separated by a semicolon (;).
$ date ; pwd
Commands can be grouped into one input/output stream by putting curly braces ({ }) around them.
$ { echo Print date: ; date ; cat cities; } | lpr
Commands can be executed in a subshell by putting round braces () around them.
$ ( echo Print date: ; date ; cat cities ) | lpr
Shell variables
Variables are part of the shell you are running. A variable has a unique name. To assign a value to a variable use variable=value .
The first character must not be a digit. No blank spaces are allowed around the "=" sign.
Examples:
$ var1="Hello class"
$ var2=2
To reference the value of a variable, use $variable.
$ echo $var1
Hello class
$ echo $var2
2
Presenter Notes
变量是脚本语言的核心,shell脚本又是无类型的。变量本质上存储数据的一个或多个计算机内存地址,分为本地变量(用户当前shell生命期使用,随shell进程的消亡而无效,类似局部变量)、环境变量(适用于所有由登录进程所产生的子进程)和位置参数(向shell脚本传递参数,只读)。而shell使用变量就需要引用,它们密切相关。
Exporting shell variables
The export command is used to pass variables from a parent to a child process by putting it in the environment of the child process.
Changes made to variables in a child process do not affect the variables in its parent.
$ export x=123
$ y=456
$ bash
$ echo $x $y
123
$ x=hello
$ y=nihao
$ echo $x $y
hello nihao
$ exit
$ echo $x $y
123 456
Presenter Notes
在shell中执行程序时,shell会提供一组环境变量。export可新增,修改或删除环境变量,供后续执行的程序使用。export的效力仅及于该次登录操作。
Standard shell variables
The shell uses several shell variables internally.
These variables are always written in uppercase.
Examples include the following:
$: PID of current shell
PATH: Path which is searched for executables
PS1: Primary shell prompt
PS2: Secondary shell prompt
PWD: Current working directory
HOME: Home directory of user
LANG: Language of user
Overwriting these and other system variables by accident can cause unexpected results. Use lowercase variables in your shell scripts to avoid conflicts.
Return codes from commands
A command returns a value to the parent process. By convention, zero means success and a non-zero value means an error occurred.
A pipeline returns a single value to its parent.
The environment variable question mark (?) contains the return code of the previous command.
$ whoami
tux1
$ echo $?
0
$ cat fileA
cat: fileA: No such file or directory
$ echo $?
1
Presenter Notes
在 Linux 下,不管你是启动一个桌面程序也好,还是在控制台下运行命令,所有的程序在结束时,都会返回一个数字值,这个值叫做返回值,或者称为错误号 ( Error Number )。
Quoting metacharacters
When you want a metacharacter not to be interpreted by the shell, you need to quote it. Quoting a single character is done with the backslash (\).
$ echo The amount is US\$5
The amount is US$5
Quoting a string is done with single (') or double (") quotes. Double quotes allow interpretation of the dollar sign ($), backtick (`), and backslash (\).
$ amount=5
$ echo 'The amount is $amount'
The amount is $amount
$ echo "The amount is $amount"
The amount is 5
Quoting non-metacharacters
The backslash can also be used to give a special meaning to a non-metacharacter (typically used in regular expressions).
\n: New line
\t: Tab
\b: Bell
A backslash followed directly by Enter is used for line continuation. The continued line is identified with the $PS2 prompt (default: >).
$ cat/home/tux1/mydir/myprogs/data/information/letter\
> /pictures/logo.jpg
Aliases
The alias command allows you to set up aliases for often-used commands. For example:
$ alias ll='ls -l'
$ alias rm='rm -i'
To show all currently defined aliases:
$ alias
To delete an alias:
$ unalias ll
$ ll
bash: ll: command not found
Presenter Notes
1、linux系统下aliases是给命令指定别名的命令作用。 2、在linux系统中如果命令太长又不符合用户的习惯,那么可以为它指定一个别名。虽然可以为命令建立“链接”解决长文件名的问题,但对于带命令行参数的命令,链接就无能为力了。而指定别名则可以解决此类所有问题
Unit review
- The shell is the command interpreter.
- A shell has a number of additional features, such as wildcard expansion, alias expansion, redirection, command grouping, and variable expansion.
- Metacharacters are a number of characters that have a special meaning to the shell. Reserved words are words that have a special meaning to the shell.
Presenter Notes
符号 英文名 中文名
~ tilde or swung dash 波浪字符或代字号
! exclamation mark 惊叹号
@ at sign or commercial at 爱特或小老鼠
# hash sign, pound, number sign 井号
$ dollar sign 美元符
% percent sign 百分号
^ caret 脱字符
& ampersand 与和符
* asterisk 星号
() parentheses, round brackets, soft brackets,
or circle brackets 小括号,圆括号
[] brackets (US), square brackets,
closed brackets or hard brackets 中括号,方括号
{} braces (UK and US), French brackets,
curly brackets 大括号,花括号
<> angle brackets or chevrons 尖括号
_ underscore 下划线
+ plus sign 加号
− minus sign 减号
= equals sign 等号
< less-than sign 小于号
> greater-than sign 大于号
. period, full stop or dot 句号,点
, comma 逗号
: colon 冒号
; semicolon 分号
? question mark 问号
- hyphen 连字符
... ellipsis 省略号
– dash 破折号
/ slash, forward slash 斜线
\ backslash 反斜线
| vertical bar 竖线
" double quote(s), quotation mark 双引号
' single quote(s), apostrophe 单引号,省略符号
` backtick(s) 反引号
References
- Unit 8: Shell basics, Linux Basics and Installation , ERC 7.2, IBM