Unit 2.3 File systems
Presenter Notes
What is a filesystem
Objectives
- What is a filesystem?
- The virtual filesystem
- Filesystem types
- A typical filesystem: ext2
- How to avoid the overuse of filesystem?
What is a filesystem?
- Place to store files and refer to them
- Hierarchical structure through use of directories
- A filesystem can be stored on any block device
- Floppy disk
- Hard disk
- Partition
- RAID, LVM volume
- File (for use with a loop device)
- RAM disk
Presenter Notes
文件系统是一种存储和组织计算机数据的方法,它使得对其访问和查找变得容易,文件系统使用文件和树形目录的抽象逻辑概念代替了硬盘和光盘等物理设备使用数据块的概念,用户使用文件系统来保存数据不必关心数据实际保存在硬盘(或者光盘)的地址为多少的数据块上,只需要记住这个文件的所属目录和文件名。
The virtual filesystem
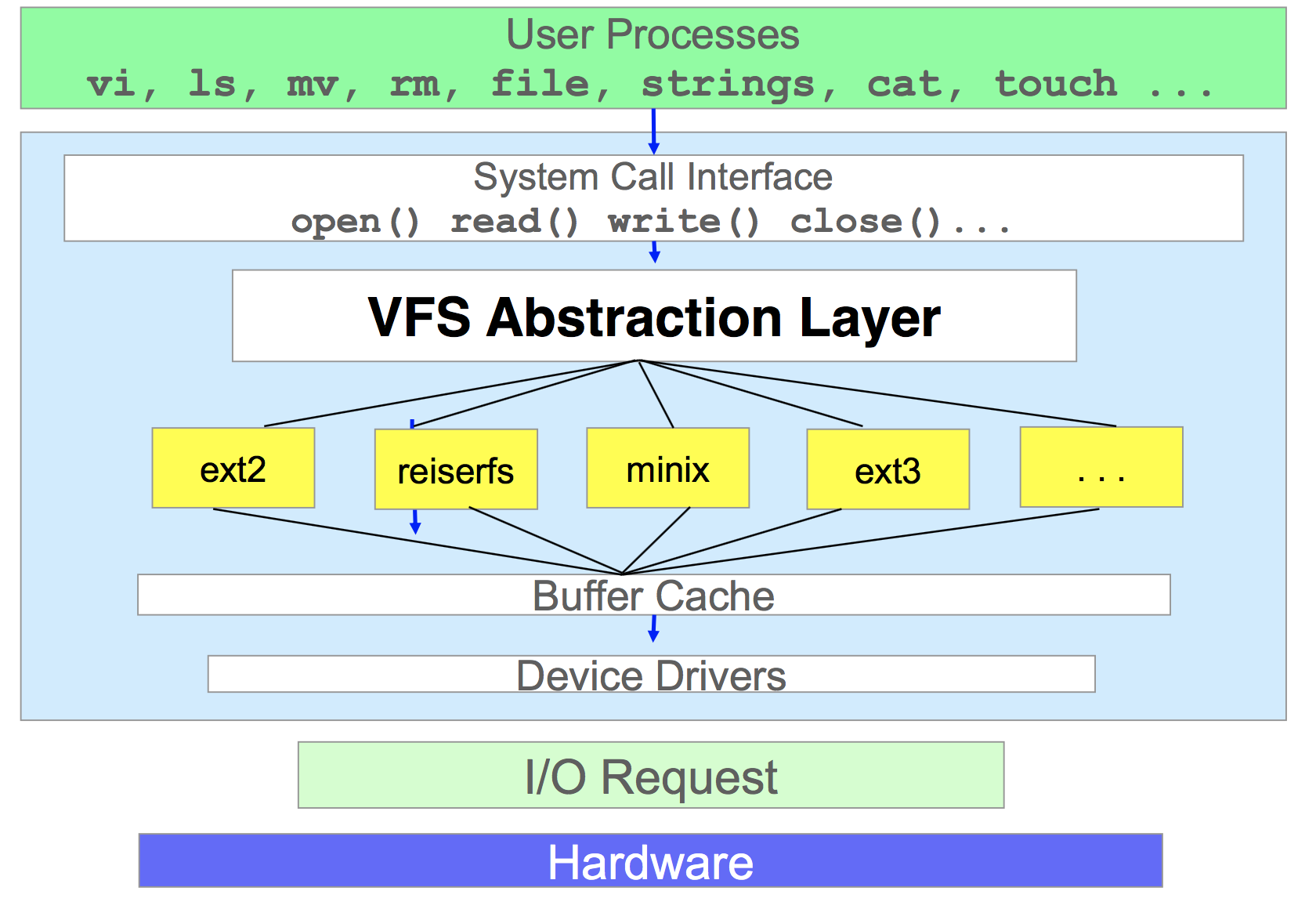
Presenter Notes
文件系统是一种用于向用户提供底层数据访问的机制,是一套实现了数据的存储、分级组织、访问和获取等操作的抽象数据类型
Filesystem types
- UNIX / Linux
- minix, ext2, ext3, ext4
- ReiserFS, IBM JFS, xfs
- Windows
- FAT-12, FAT-16, FAT-32, exFat -- vfat
- NTFS
- CD-ROM ISO 9660
- Network
- NFS (Network File System)
- SMBFS (Windows share)
- Virtual
- SHMFS (Shared Memory Filesystem)
Presenter Notes
Windows从NT内核(即win2000之后)开始使用NTFS文件系统;
部分Linux发行版默认不支持NTFS文件系统,解决方法是安装ufsd等NTFS驱动程序。
Filesystem example: ext2
Partition divided into blocks of 1024, 2048 or 4096 bytes
- Blocksize depends on size of filesystem and expected usage
Blocks can have different usage:
- Superblock
- Index node (inode) block
- Indirect block (double, triple)
- Data block

Presenter Notes
ext2文件系统由Rémy Card设计,用以代替ext,于1993年1月加入linux核心之中。它和BSD中的Unix文件系统具有相同的设计标准,同时也是Linux上的第一个商业级文件系统。
Superblock
- First block of filesystem, several copies (at 8193, 16385, ...)
- Contains general info on filesystem
- Last mounted time/place
- Block size
- Pointers to free inodes
- Pointers to free blocks
- Pointer to root of filesystem
Presenter Notes
使用mount命令时,在指定机器上被挂载的文件系统都会在super_blocks[]表格中以super_block的形式表现出来
Tunable parameters
- The most important components of a filesystem are the inodes and the data blocks
- The filesystem is full if:
- No more inodes are available
- No more data blocks are available
- So tune your filesystem according to the number of bytes per file:
- Blocksize (1024, 2048, or 4096 possible)
- Bytes-per-inode (4096 default)
Quota concepts
- Quotas limit the amount of data a user/group is allowed to store
- Defined on a per-filesystem basis
- Based on block and/or inode usage per user or group
- Two limits per quota: Soft and hard
- User exceeds soft limit: warning only
- User exceeds hard limit: error
- Grace period identifies how long the soft limit may be exceeded
- After that period, a user gets errors instead of warnings

Presenter Notes
quota 命令显示磁盘使用情况和限额。缺省情况下,或者带 -u 标志,只显示用户限额。quota 命令报告 /etc/filesystems 文件中列出的所有文件系统的限额。
Summary
- Filesystem is the place to store files and directories.
- A filesystem has a root directory and hierarchical structure of directories.
- Use the virtual filesystem to unify the usage of different filesystem types.
- A typical filesystem: ext2
- Use quota to limit the usage of a filesystem.
Using a filesystem
Objectives
- How to connect a file system?
- What's a mount point?
- How to disconnect a file system?
Mount
mount is the glue that logically connects file systems to the directory hierarchy
File systems are associated with devices represented by special files in /dev
When a file system is mounted, the volume and its contents are connected to a directory in the hierarchical tree structure
mount [what to mount] [where to mount]
eg. # mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
Presenter Notes
mount指令是告诉操作系统,对应的文件系统已经准备好,而该文件系统会对应到一个特定的点(称为挂载点)。挂载好的文件、目录、设备以及特殊文件即可提供用户使用。
Mounting over an empty directory
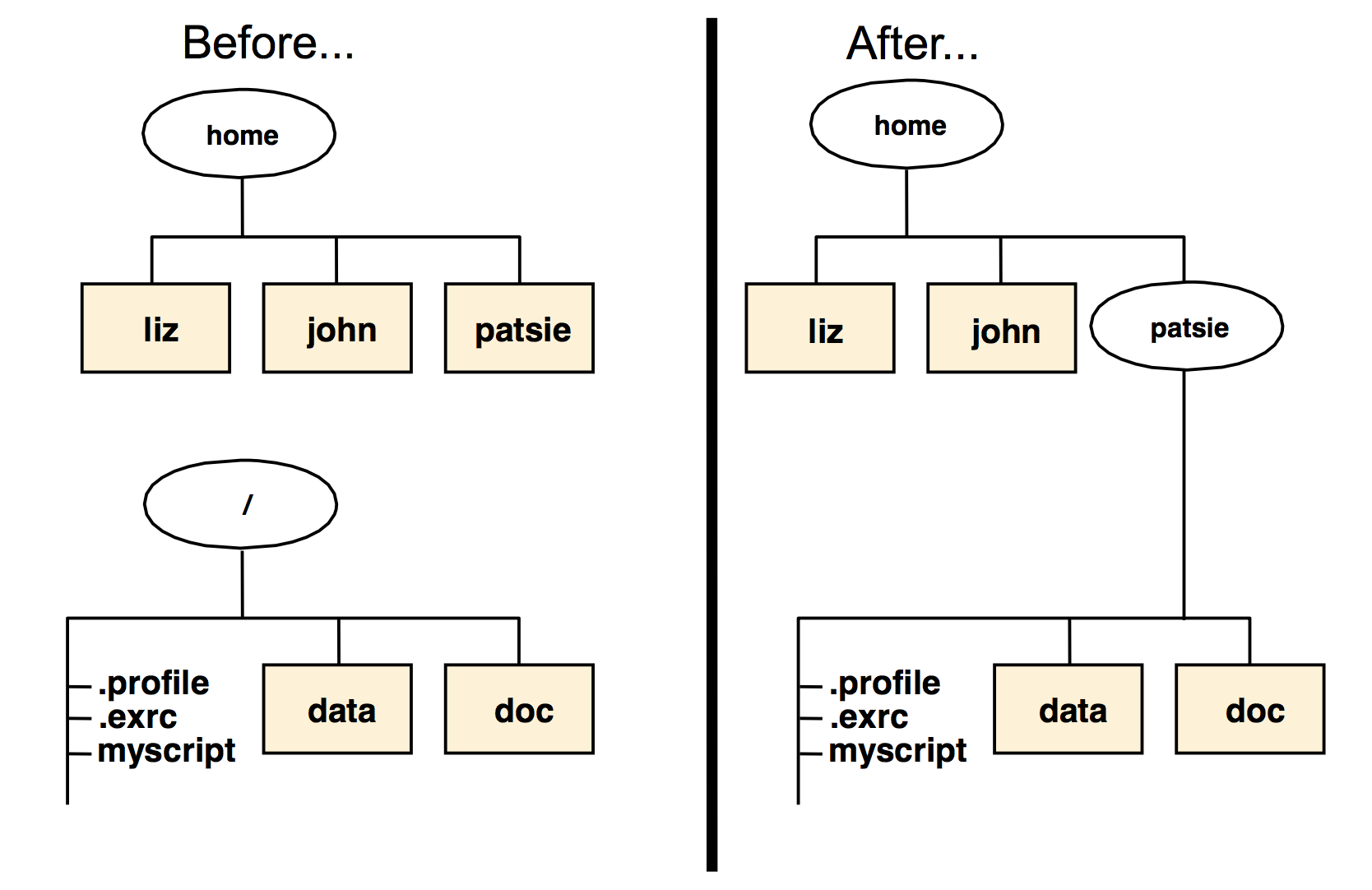
Mounting over files
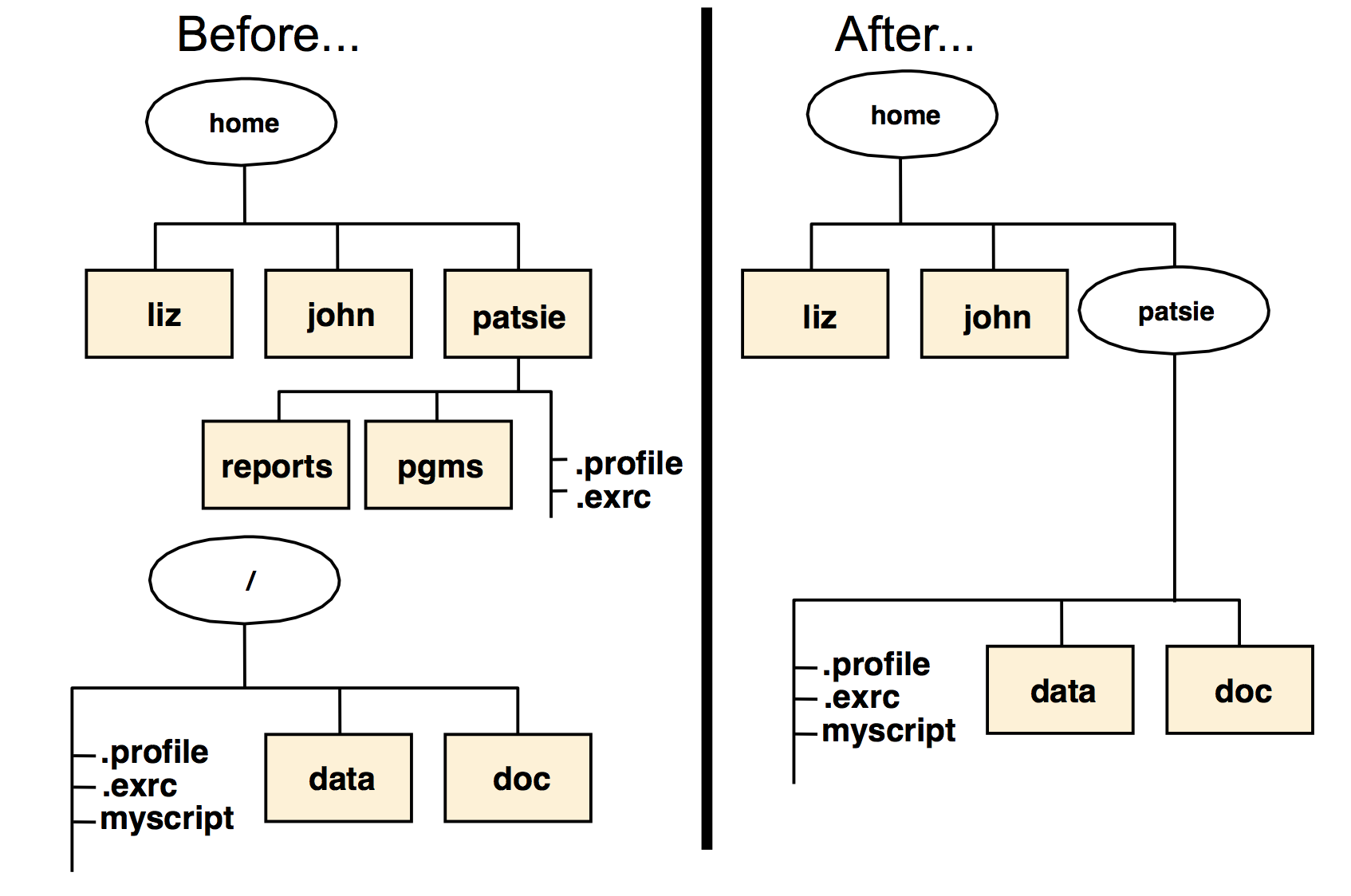
umount
Use the umount command with either the device name or the mount point, or both
eg. umount /dev/sda1
-or- umount /mnt
Summary
mountis the glue to connect a file system.- Mount point is where a file system connected to.
- After use a file system, remember to
umountit.
Backup and restore
Objectives
- Backup schemes
- Backup tools
Backup schemes
- Full backup
- Preserves the whole system
- System backup
- Preserves system directories and files
- Data backup
- Preserves user data
- Incremental or differential backup
- Only backup files that changed
- Very fast, but takes more time to restore
Presenter Notes
- 完全备份(Normal):备份所有选择的文件和文件夹(不管是否被设为存档属性),备份后清除备份标志
- 增量备份(Incremental):只备份选择的,并且带有标志的文件和文件夹,它清除备份标志,只备份上次正常备份或增量备份以来创建或更改的文件。
- 差异备份(Differential):只备份选择的,并且带有标志的文件和文件夹,它不清除备份标志,也只备份上次正常备份或增量备份以来创建或更改的文件。
Incremental versus differential backup
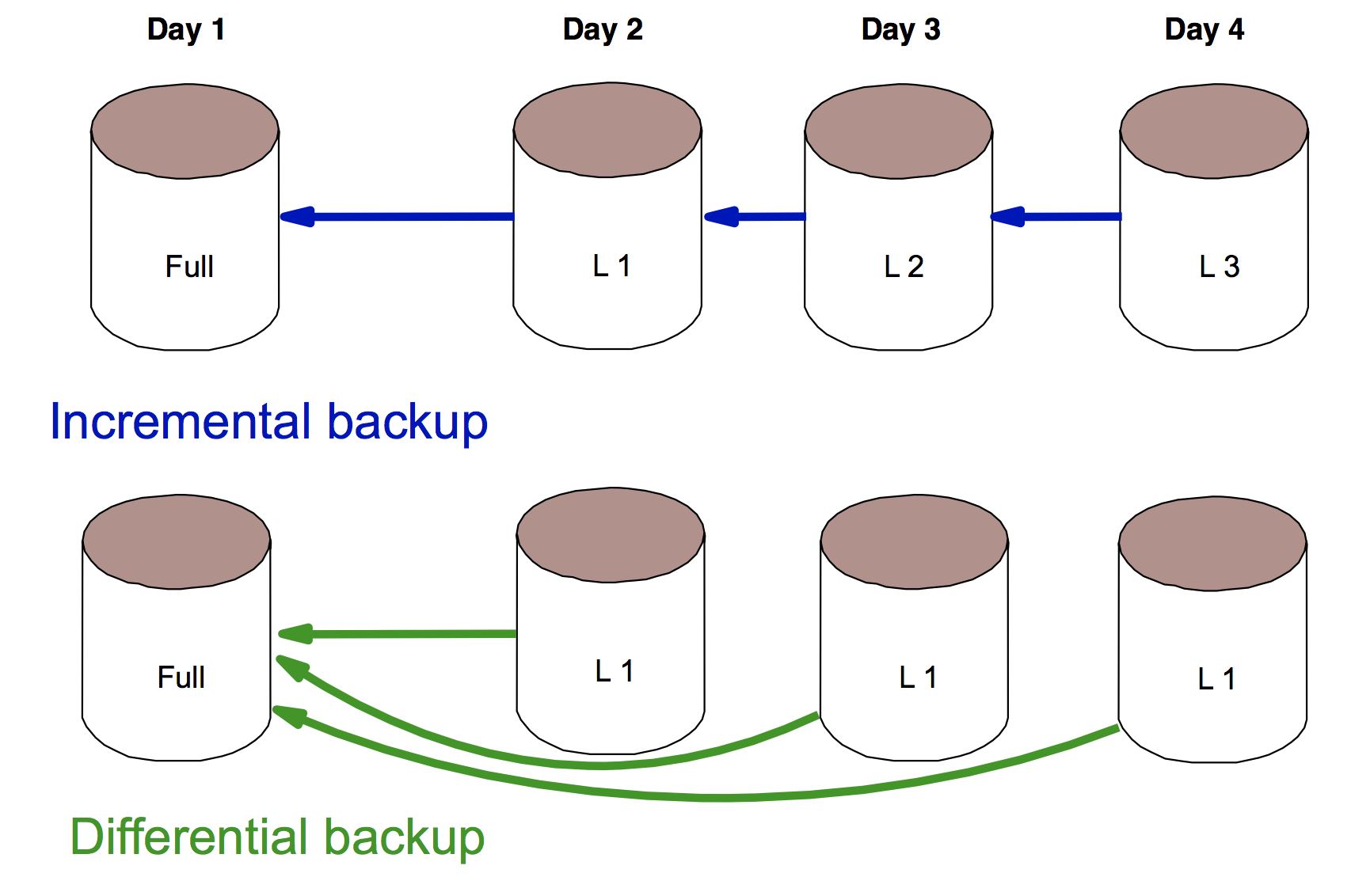
Presenter Notes
备份是容灾的基础,如果系统的硬件或存储媒体发生故障,备份可以帮助保护数据免受损失。
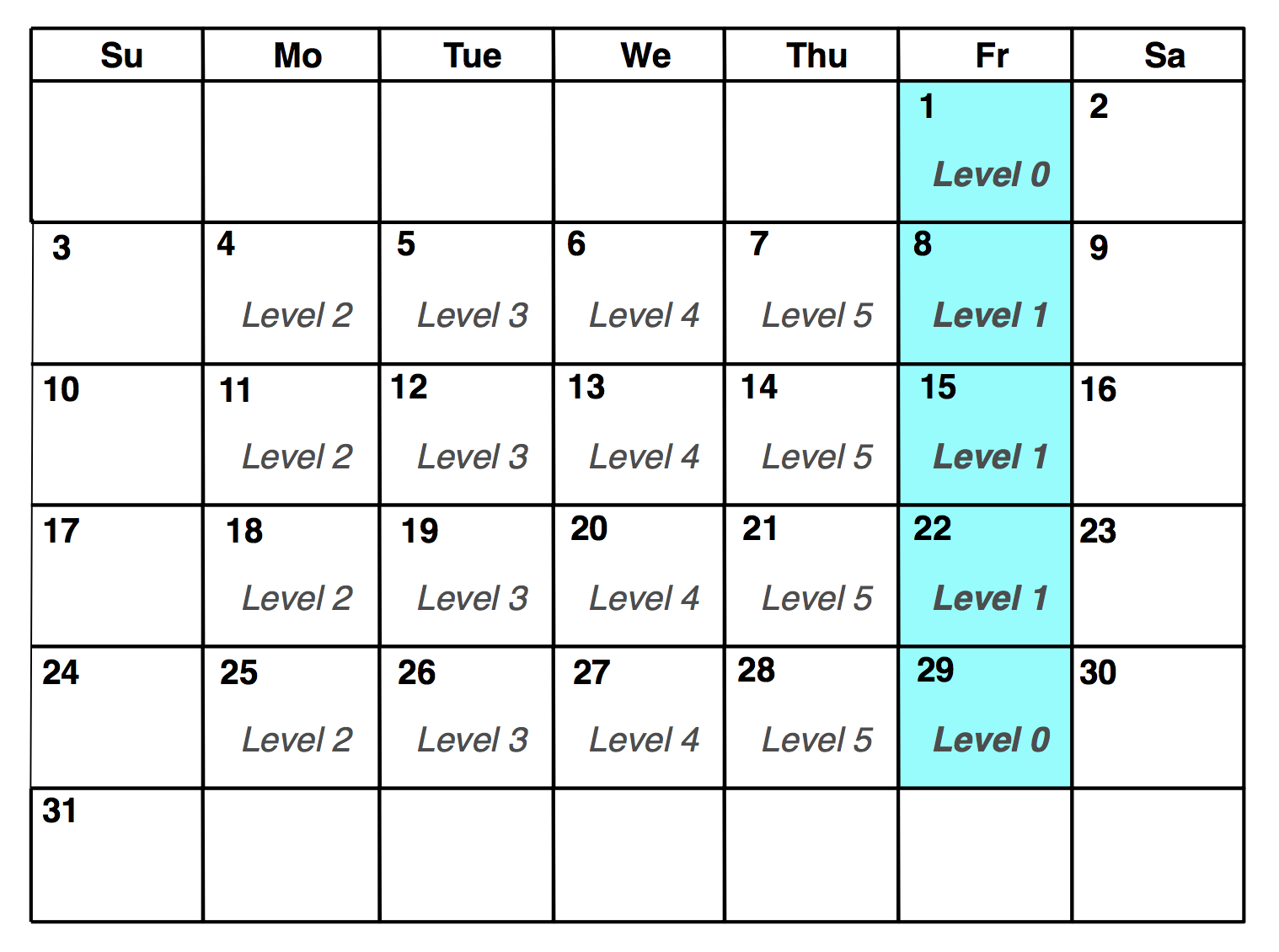
Sample monthly backup scheme
tar command
- Traditional UNIX tape archive command
- Backup with tar:
# tar -cvf home.tar /home - Restore with tar:
# tar -xvf home.tar [ files to extract ] - List contents of a tar backup:
# tar -tvf home.tar - The GNU version of tar has a lot of improvements:
compression : use z option (gzip) or j option (bzip2)
# tar -zcvf home.tar.gz /home
# tar -jcvf home.tar.bz2 /home
Presenter Notes
Unix和类Unix系统上的压缩打包工具,可以将多个文件合并为一个文件。tar文件格式已经成为POSIX标准,最初是POSIX.1-1988,目前是POSIX.1-2001。
dd command
- Command to make bit-for-bit dumps of files, filesystems, and disks
- To make a full disk backup image and restore it again:
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/mnt/nfs/sda.img bs=1M
# dd if=/mnt/nfs/sda.img of=/dev/sdc bs=1M - To make a backup of your MBR:
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/mnt/nfs/mbr.img bs=512 count=1 - To trash your system thoroughly:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1M
# dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sda bs=1M
Presenter Notes
dd命令主要功能为转换和复制文件,也可以用在备份硬件的引导扇区、获取一定数量的随机数据等任务中
Summary
- Backup schemes:
- full backup
- system backup
- data backup
- incremental backup
- differential backup
- Backup tools:
- tar
- dd
References
- Chapter 4: Filesystems, Modern Operating Systems . Forth Edition, Andrew S. Tanenbaum
- Unit 10: File systems and file system quota, Linux System Administration, ERC 7.2, IBM
- Unit 13: Backup and Restore, Linux System Administration, ERC 7.2, IBM